Command templates
Last updated on
Once you enabled the Run Command Service, you want to get the information about the currently available commands for you to use.
The following documentation describes how you can retrieve all currently available and supported command templates in the STACKIT Portal in order to use them for remote run on your server.
Using command templates via the portal
Section titled “Using command templates via the portal”Use the following steps, if you want to use the STACKIT Portal in order to get the information about the currently available command templates:
In your project navigate to the overview of your server you want to run a command remotely at and click on “Commands” → “Templates” to find a list of all available command templates for this server:
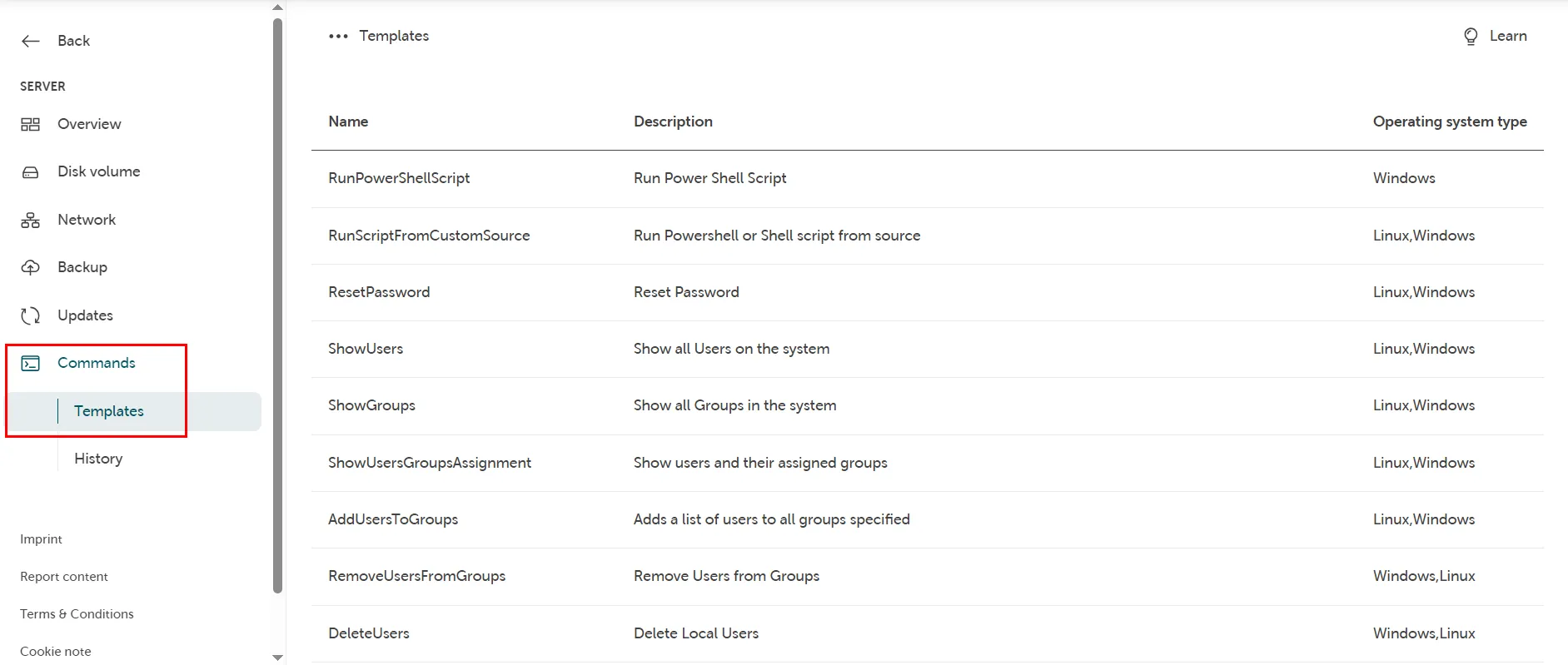
Click on a command template (i.e. “ShowUsers”) and it will display an info box with details about the supported operating system (Linux/Windows) as well as the content of the script you ran:
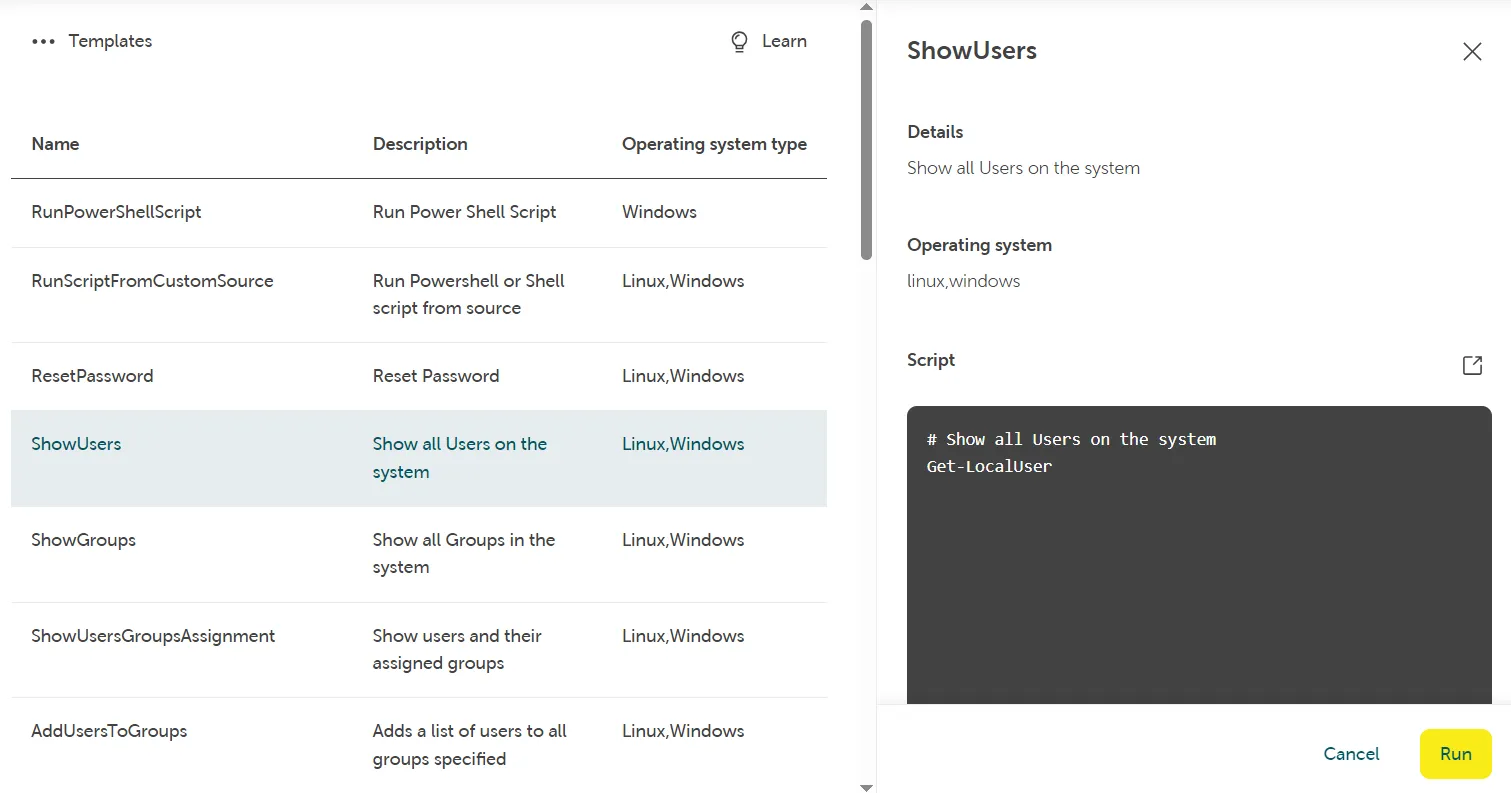
List of command templates
Section titled “List of command templates”| Number | OS Type | Command Template Name | Command Template Title | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linux | RunShellScript | Run shell script | - | Linux: Run custom shell script on Linux servers. Example usage of arguments: - arguments: “arg1 arg2 arg3” |
| 2 | windows | RunPowerShellScript | Run PowerShell script | - | Windows: Run custom PowerShell script on Windows Servers. Example usage of arguments: - arguments: “arg1 arg2 arg3” |
| 3 | Linux/Windows | RunScriptFromCustomSource | Run script from custom stackits3, local or public source | sourceType, location | Linux: Run shell script from different custom source. Available source types:
|
| 4 | Windows: Run shell script from different custom source. Available source types:
| ||||
| 5 | Linux/Windows | ResetPassword | Reset password or create a new user | username, password | Linux: Reset password of an existing user or create a new user with sudo privileges on Linux servers. |
Windows: Reset password of an existing user or create a new administrator on Windows Servers. | |||||
| 6 | Linux | ResetSSHPublicKey | Reset SSH key or create a new user | username, key | Linux: Reset SSH Public Key of an existing user or create a new user with sudo privileges on Linux servers. |
| 7 | Linux/Windows | ShowUsers | Show all users in the system | - | Linux: Show all users in the system with user ID, group ID, home directory, shell and further information. |
Windows: Show all users in the system with description. | |||||
| 8 | Linux/Windows | ShowGroups | Show all groups in the system | - | Linux: Show all groups in the system with details. |
Windows: Show all groups in the system with details. | |||||
| 9 | Linux/Windows | ShowUsersGroupsAssignment | Show users and their assigned groups | users | Linux: Show users in the system and their assigned groups. You can specify a single user or a list of users (user1,user2,user3). |
Windows: Show users in the system and their assigned groups. You can specify a single user or a list of users (user1,user2,user3). | |||||
| 10 | Linux/Windows | AddUsersToGroups | Add users to all groups specified | users, groups | Linux: Add one or more users to one or more groups. Example usage of arguments: - users: “user1,user2,user3”- groups: “group1,group2,group3” |
Windows: Add one or more users to one or more groups. Example usage of arguments: - users: “user1,user2,user3”- groups: “group1,group2,group3” | |||||
| 11 | Linux/Windows | RemoveUsersFromGroups | Remove users from groups | users, groups | Linux: Remove one or more users from one or more groups. However, you cannot remove a user from its primary group. Example usage of arguments: - users: “user1,user2,user3”- groups: “group1,group2,group3” |
Windows: Remove one or more users from one or more groups. Example usage of arguments: - users: “user1,user2,user3”- groups: “group1,group2,group3” | |||||
| 12 | Linux/Windows | DeleteUsers | Delete local users from the system | user | Linux: Delete one or more local users from the system. Example usage of arguments: - users: “user1,user2,user3” |
Windows: Delete one or more local users from the system. Example usage of arguments: - users: “user1,user2,user3” | |||||
| 13 | windows | joinDomain | Join a Windows Server to a domain | DNS, DomainName, DomainUser, DomainPassword, OuPath | Windows: Join a Windows Server to a domain. Input arguments:
|
| 14 | Linux/Windows | ShowHostname | Show the host name | - | Linux: Show the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name). |
Windows: Show the local host name. | |||||
| 15 | Linux/Windows | ShowSystemInfo | Show system information | - | Linux: Show system information about CPU, storage, RAM, BIOS and more. |
Windows: Show system information about CPU, storage, RAM, BIOS and more. | |||||
| 16 | Linux/Windows | ShowLogEntries | Show log entries from the system | Linux: - | Linux: Show systemd journal entries with higher priority from last boot. |
Windows: Retrieve and display Windows event logs with options to filter by log names, entry type, time and date, and limit output. Available log names: Default behavior shows 10 logs per log name in chronological order. Example usage of arguments: | |||||
| 17 | Linux/Windows | ShowCurrentWorkload | Show current workload on the system | - | Linux: Provide a dynamic real-time view of the running system. |
Windows: Show the current workload (CPU and RAM utilization). | |||||
| 18 | Linux/Windows | ShowProcesses | Show processes on the system | Linux: - | Linux: Report a snapshot of the current processes. |
Windows: Show processes and their related workload. Run the script without arguments to get all processes. If you want to specify one process or a list of processes, run it with arguments. Example usage of arguments: - ProcessName: “process1,process2” | |||||
| 19 | Linux/Windows | ManageServices | Manage services on the system | action, services | Linux: Manage services and perform actions on them. Input arguments:
|
Windows: Manage services and perform actions on them. Input arguments:
| |||||
| 20 | Linux/Windows | KillProcesses | Kill processes on the system | Linux: signal, processname Windows: processname | Linux: Kill (end) a process. Input arguments:
Example usage of arguments: - signal: “SIGKILL”- processname: “process1” |
Windows: Kill (end) one or more processes. Example usage of arguments: - processname: “process1,process2” | |||||
| 21 | Linux/Windows | ShowNetworkConfiguration | Show network configuration | - | Linux: Show network interfaces configuration. |
Windows: Show IP configuration. | |||||
| 22 | Linux/Windows | ShowRouting | Show routing table entries | - | Linux: Show routing table entries. |
Windows: Show routing table entries. | |||||
| 23 | Linux/Windows | ShowSocketStatus | Show all sockets and status | - | Linux: Show all sockets and status. |
Windows: Show all sockets and status. | |||||
| 24 | Linux/Windows | ShowMemoryUsage | Show memory usage | - | Linux: Show memory and swap usage. |
Windows: Show total, used and available physical memory. | |||||
| 25 | Linux/Windows | ShowFilesystems | Show filesystems with disk usage | - | Linux: Show filesystems with disk usage. |
Windows: Show filesystems with disk usage. | |||||
| 26 | linux | ShowInodes | Show filesystems with Inodes usage | - | Linux: Show filesystems with Inodes usage. |
| 27 | linux | ShowBlockDevices | Show block devices | - | Linux: Show block devices. |
| 28 | linux | ShowPartitionsTable | Show partitions table | - | Linux: Show partitions table. |
| 29 | linux | ShowMountedFilesystems | Show mounted filesystems | - | Linux: Show mounted filesystems. |
| 30 | windows | EnableRemotePowerShell | Enable remote PowerShell | - | Windows: Configure the machine to enable remote PowerShell. |
| 31 | windows | DisableNetworkLevelAuthentication | Disable Network Level Authentication | - | Windows: Use this script to disable NLA if RDP connections are failing with error ’ The remote computer that you are trying to connect to requires Network Level Authentication (NLA), but your Windows domain controller cannot be contacted to perform NLA. ’ or error ’ An authentication error has occurred. The Local Security Authority cannot be contacted. ’ NLA is a security feature that should only be disabled temporarily to allow RDP connections to succeed until the domain controller connectivity issue has been resolved. |
| 32 | windows | ShowRDPSettings | Show RDP listener settings | - | Windows: Show detailed information about the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway for each adapter bound to TCP/IP. |
| 33 | windows | ResetRDPCertificate | Reset RDP certificate to default | - | Windows: Remove the SSL certificate tied to the RDP listener and restores the RDP listener security to default. Use this script if you see any issues with the certificate. This script will restart the TermService. |
| 34 | windows | EnableRDPPort | Configure Remote Desktop port | RDPPort | Windows: Set the default port number (3389) or user specified port number for Remote Desktop connections and enable firewall rule for inbound access to the port. Example usage of arguments: - RDPPort: “3389” |