Running custom scripts
Last updated on
How to enter and run a custom script
Section titled “How to enter and run a custom script”-
Use one of the following two command templates depending on your server OS:
RunShellScript(Linux)RunPowerShellScript(Windows)
-
Enter your custom script in the Script field of the pop up window on the right. The maximum length of your script content is 10.000 characters. You can also use the expanded script overview button for better code readability.
-
Enter the arguments, if any. Separate multiple arguments with blank characters.
-
Press Run.
Types of shell scripts that can be run on Linux
Section titled “Types of shell scripts that can be run on Linux”For Linux there are different ways to run a shell script depending on whether an argument and/or a shebang header is present.
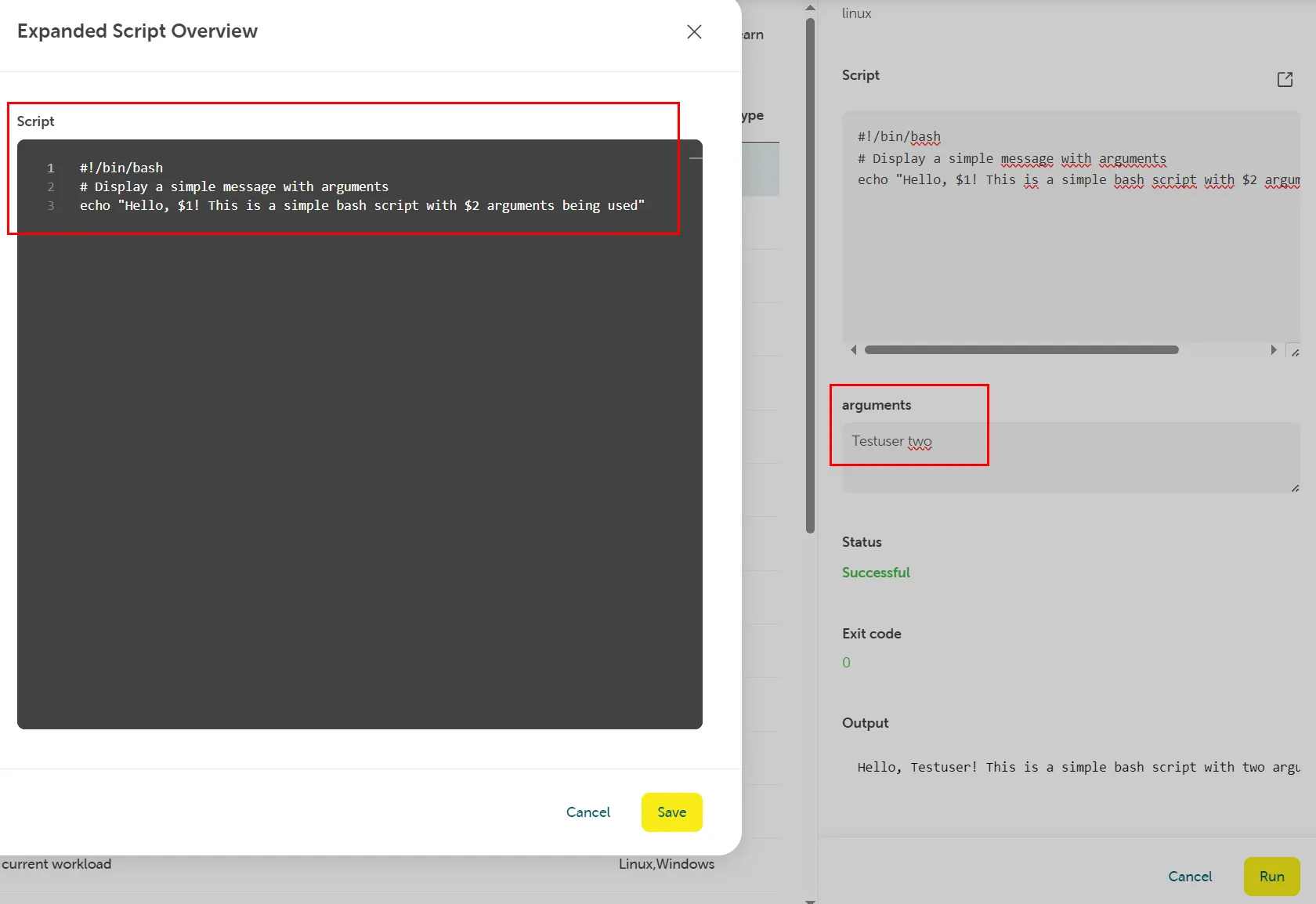
Script with shebang header and arguments
Section titled “Script with shebang header and arguments”A script with both shebang header and arguments will be run as bash script.
Example script:
#!/bin/bash# Display a simple message with argumentsecho "Hello, $1! This is a simple bash script with $2 arguments being used"Arguments: Testuser two
Script with shebang header and no arguments
Section titled “Script with shebang header and no arguments”A script with shebang header, but without arguments will be run with the given shebang interpreter.
Make sure the path to the interpreter in the shebang is correct when running the script via Run Command. In order to run i.e. a Python script like in the example below, Python needs to be properly installed on the server before you run the script.
Example script:
#!/bin/python3# Display a simple messageprint("Hello, world! This is a simple python script without arguments being used")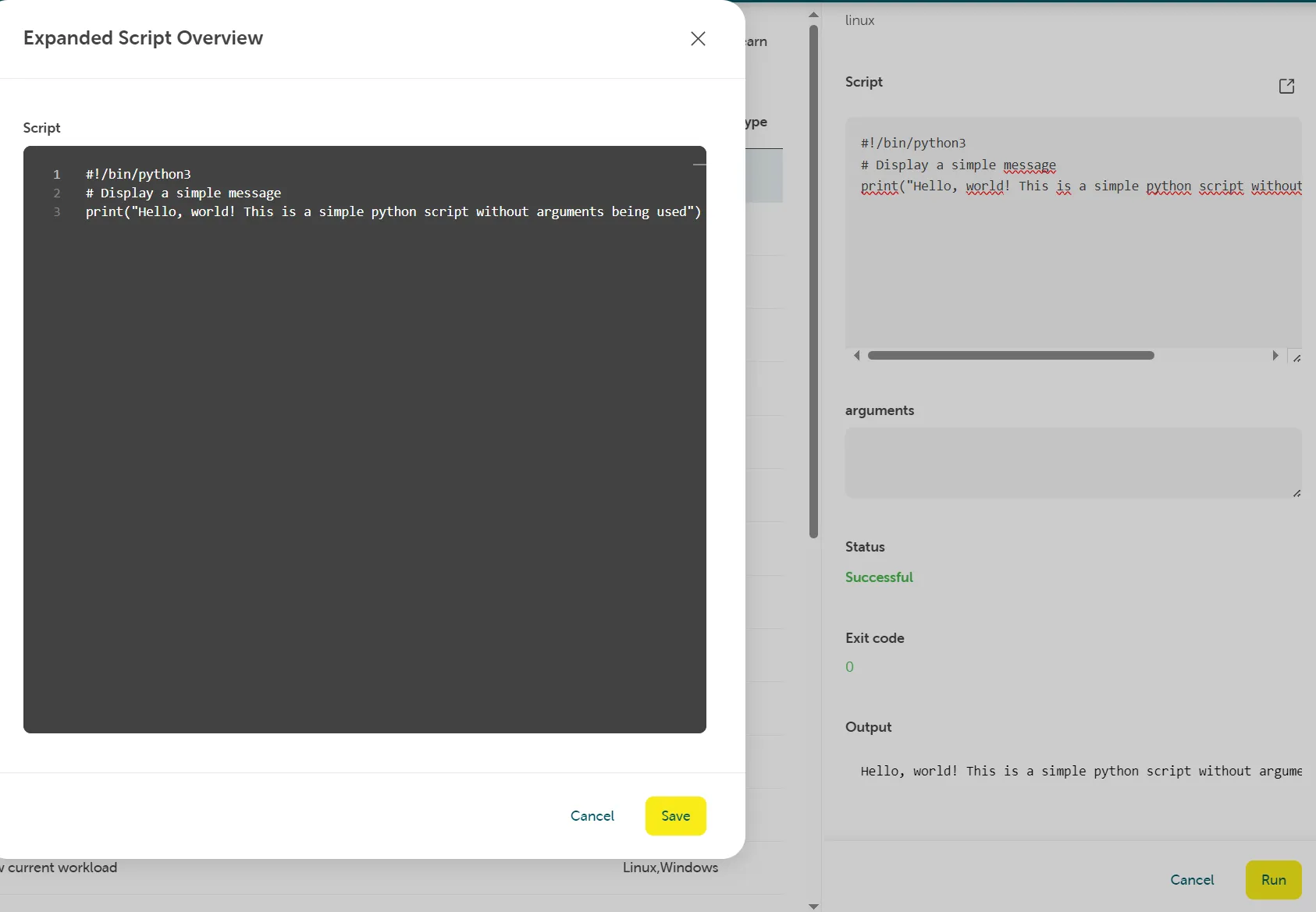
Script without shebang header
Section titled “Script without shebang header”A script without shebang will be run as bash script.
Example script (displays system information):
echo "System Info: $(uname -a)"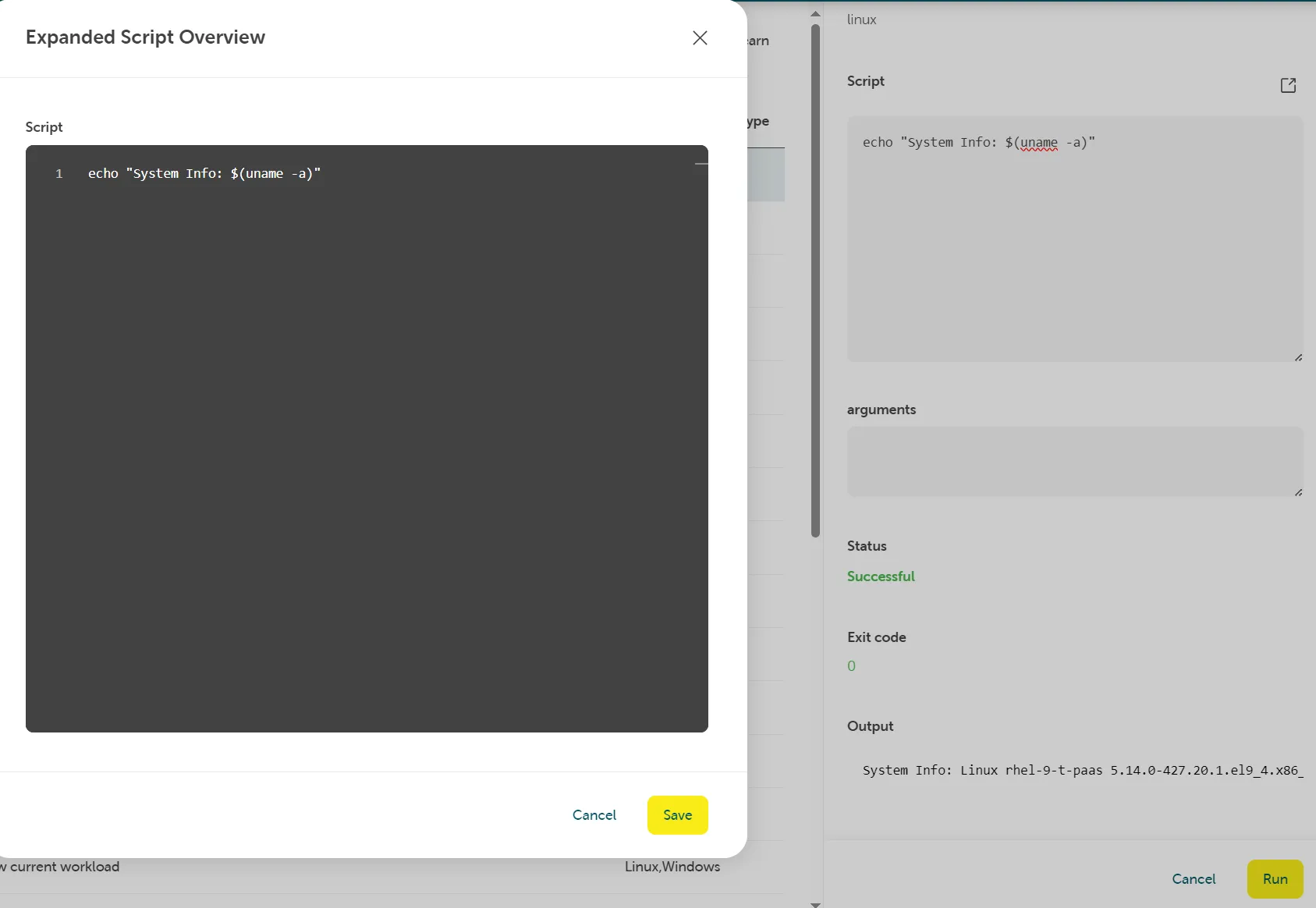
Examples
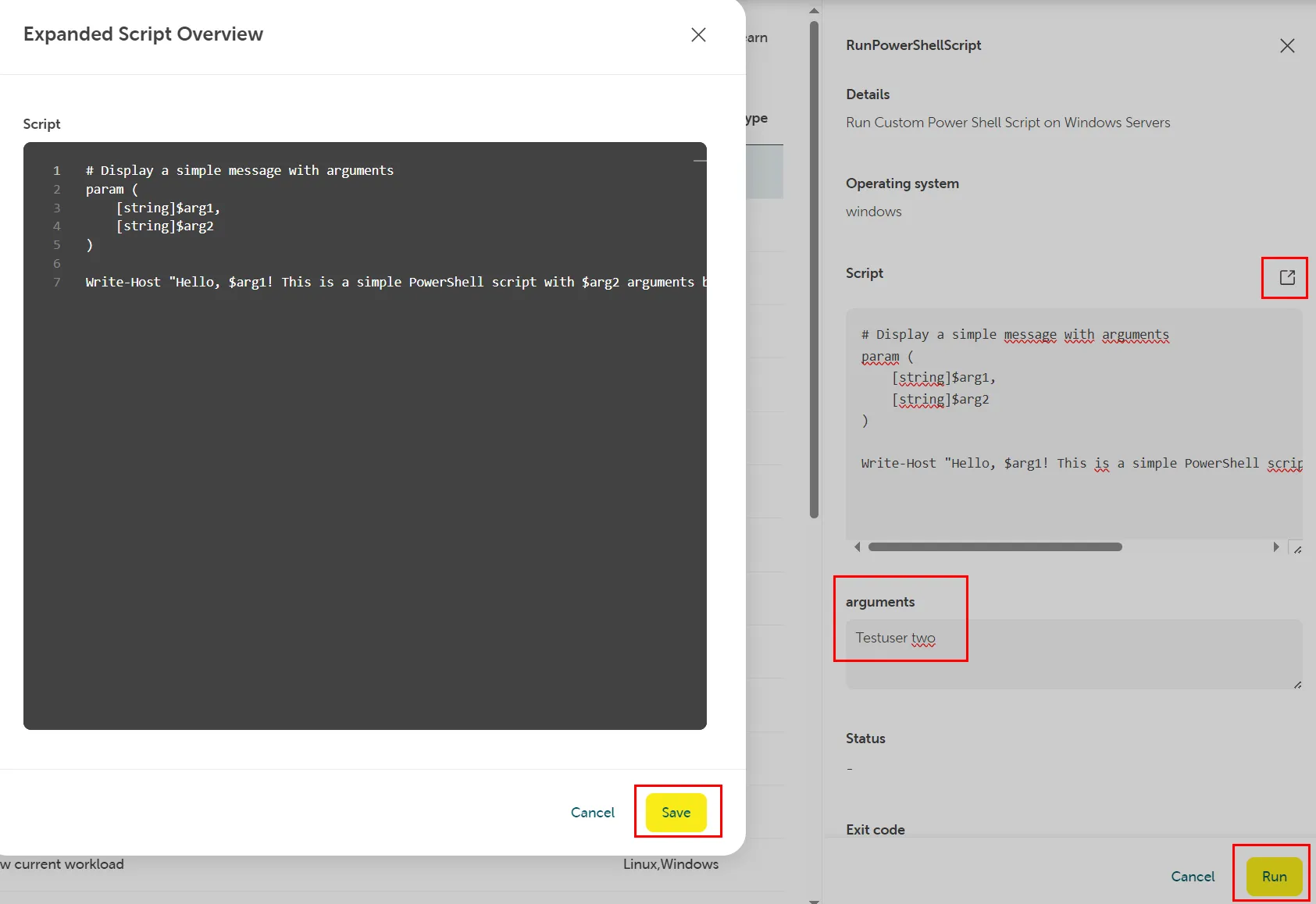
Section titled “Examples”Custom script on a Windows Server VM
Section titled “Custom script on a Windows Server VM”In this example we run a simple script to show a message with some arguments on a Windows Server.
Example script:
param ( [string]$arg1, [string]$arg2)
Write-Host "Hello, $arg1! This is a simple PowerShell script with $arg2 arguments being used"Arguments: Testuser two
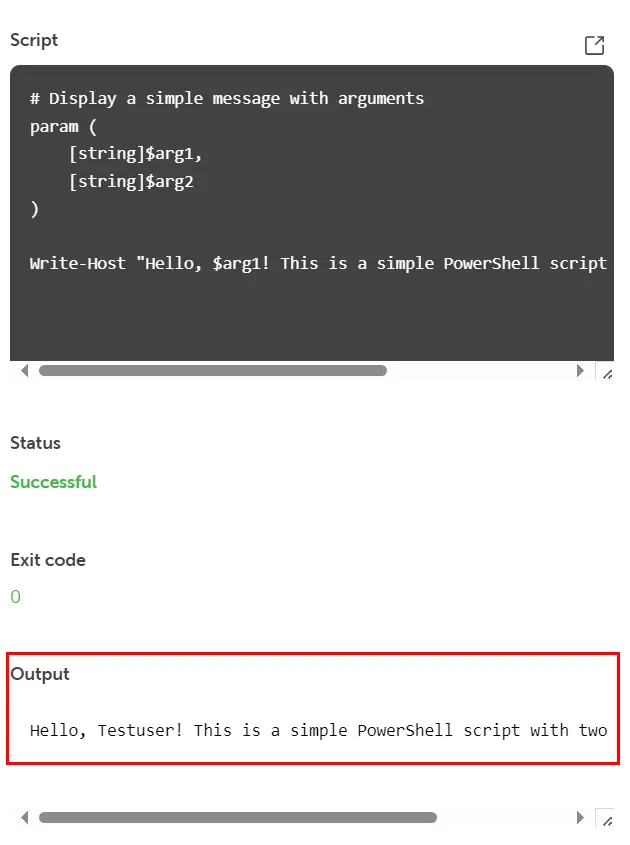
The Output contains the desired result value with the arguments included:
Custom script on a Linux VM
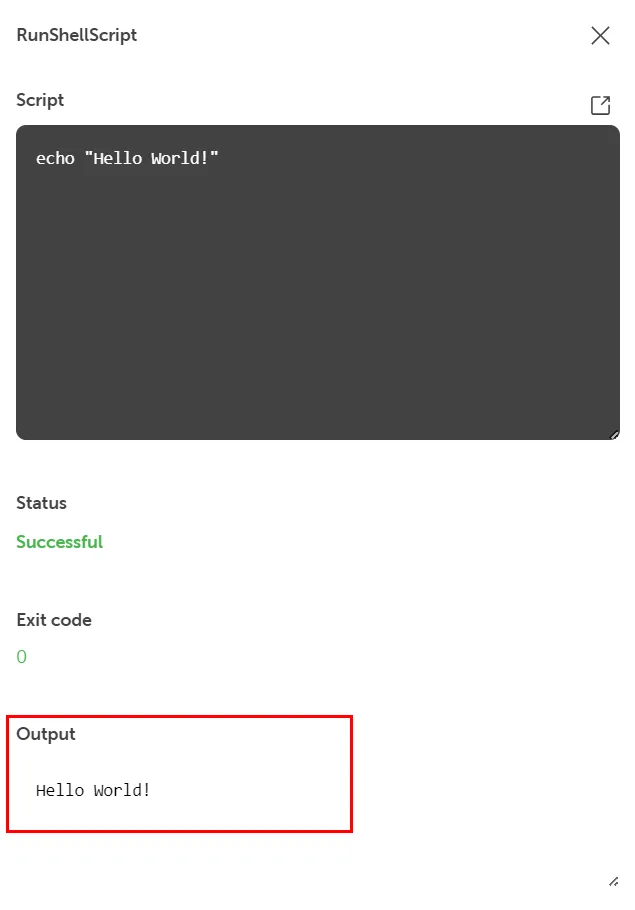
Section titled “Custom script on a Linux VM”In this example we run a simple “Hello World” script on a Linux Server:
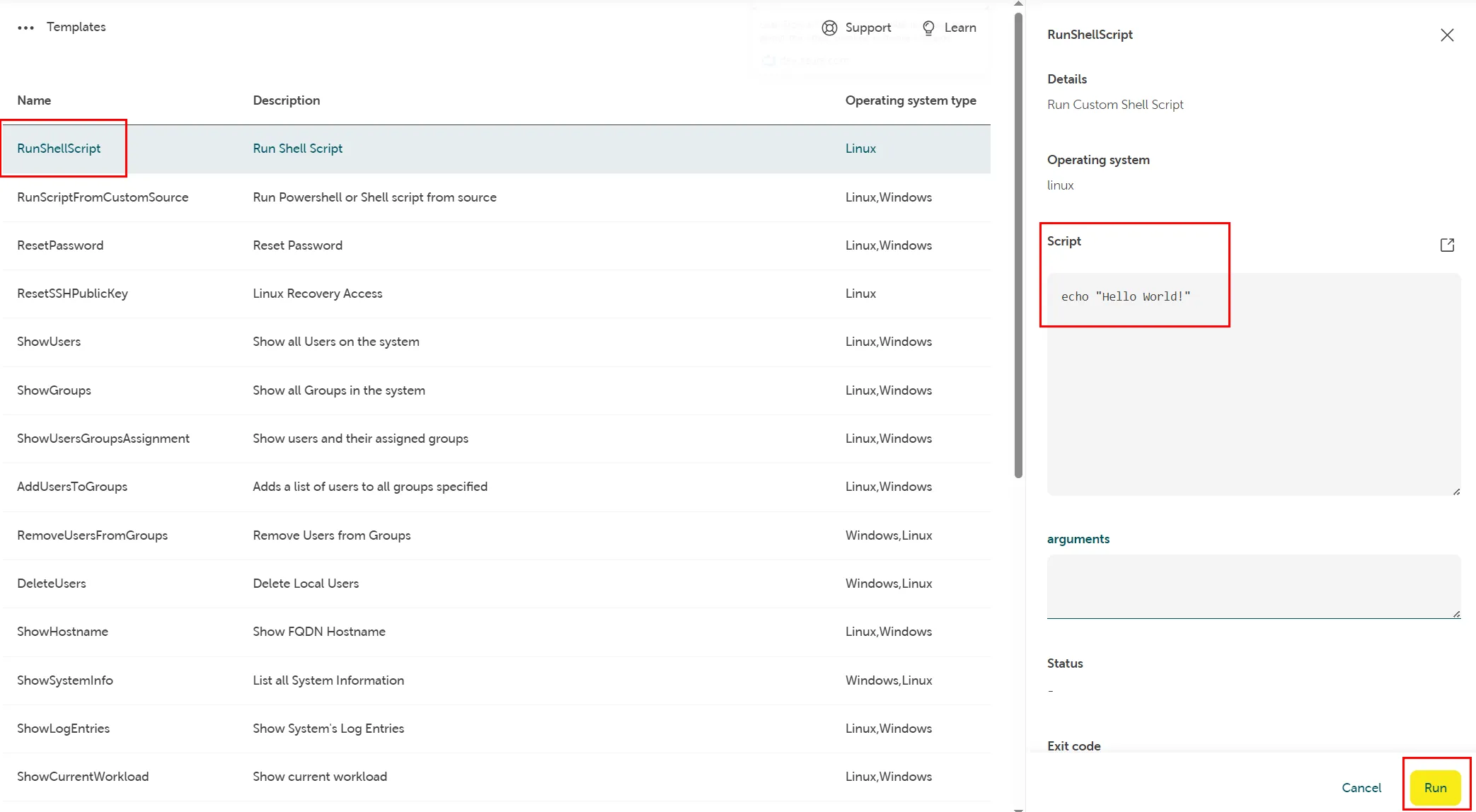
Also here the Output contains the desired result value “Hello World!”: