FAQ
Last updated on
-
General
What are the default management settings which are applied to my Windows Server?
Default management strategy will be automatically applied on each new Windows Server. This strategy includes:
- daily backup for all volumes which are attached to this server which is kept for 14 days.
- check for and install of new Windows updates during the weekend. Backup before update installation will be done automatically and will be available in the next 14 days.
I can not RDP into my new Windows Server
Please, make sure that you have configured the additional security layer as described here.
What is the Scanning Agent for SPLA reporting?
STACKIT is responsible for reporting monthly licensing usage of the customers to Microsoft under the Service Provider Licensing Agreement (SPLA). In order to do this on every Windows Server, the Octopus Reporting Agent is installed, which is scanning the Microsoft products installed on each server once per day.
The customer is responsible to ensure that this program will not be uninstalled and the scheduled tasks to run will not be disabled, changed or removed. Upon request, customers must cooperate with STACKIT to fix issues with the Octopus Reporting Agent or must provide STACKIT temporary access to these servers to fix them.
STACKIT will investigate and remedy any potential non-compliance and that is why if a non-licensed software is installed on Windows Servers – STACKIT will inform the customer that this software need to be uninstalled or license need to be provided.
What is the Scanning Agent for SPLA reporting?
The STACKIT Server Agent is running on each STACKIT Server and is a crucial service to provide our current and future STACKIT features and services like Run Command, Server Update Management and many more to come. It serves as an interface between our infrastructure and the operating system and receives and processes scripts sent remotely and executes them locally on your server, allowing you to configure your server as required.
The customer is responsible to ensure that this program will not be uninstalled and the scheduled tasks to run will not be disabled, changed or removed. Upon request, customers must cooperate with STACKIT to fix issues with the Octopus Reporting Agent or must provide STACKIT temporary access to these servers to fix them.
You can find more information about the STACKIT Server Agent here: STACKIT Server Agent
What is Cloudbase-Init?
We use Cloudbase-Init - its main role is setting up the initial password for the server, but its functionality is far beyond that. For example, the service will start every time your computer is restarted, check for possible MTU adjustments, unallocated free space for the current volume and other maintenance and management features. Once finished the service is automatically set in a stopped state to prevent any overhead for the system.
Useful information about the RRULE format
Where is my server volume backup stored?
All server volume backups (Cinder) are stored on a backup storage system in one availability zone and are asynchronously replicated to a second, independent backup storage system in another availability zone. This applies to all backups, no matter if it the source is a single availability zone or metro volume. I.e. backups of a volume in a single availability zone are replicated as well.
Current known issues in BETA phase
The
Credential Guardsecurity feature cannot be enabled at the moment. This is because the current images do not support the required prerequisites UEFI BIOS with enabledSecure Bootand support for Virtualization-based security, see requirements. Also on hypervisor level (virtual) TPM modules are currently not implemented, which are a recommended prerequisite for using above mentionedCredential Guard, and which also prevents security features likeBitLockerfrom working properly, see system requirements. It is planned to update the images to fully support the above mentioned requirements in the future. -
Licensing
Can I bring my own Windows Server licenses to STACKIT?
Yes you can bring your own Windows Server licenses to STACKIT if you upload and use your own customized images in OpenStack, have Software Assurance for it and follow the rules which are documented here.
Can I buy Windows Server licenses from STACKIT?
STACKIT only provides Virtual Machines with Windows Server operating system as a Service and does not resell any licenses.
Why I need a Windows Server Remote Desktop Services User Subscriber Access License (RDS SAL) for each local user?
If you use Standard STACKIT Windows image, according to latest Services Provider Use Rights, for each end user who is authorized to access to a Windows Server regardless of the purposes of this access a Remote Desktop Service User Subscriber Access License (SAL) is required
How STACKIT will charge me for the Windows Server Remote Desktop Services SALs?
If you use Standard STACKIT Windows image, STACKIT will monitor the number of required licenses with a scanning agent installed on every Virtual Machine. For each user who is authorized to access the server a license will be included in your invoice.
Can I Bring my Remote Desktop Services (RDS) CALs to STACKIT?
Yes you can bring it if you have Software Assurance for it and you follow the rules which are documented here.
Can I change my RDS CAL per device to a per user one?
Yes, if your RDS CALs are under Software Assurance you can convert them when renewing your agreement. Please contact Procurement, your Software Reseller or Microsoft Partner.
-
Others
Octopus Agent is sending no Data
Cause of the Problem
Section titled “Cause of the Problem”All STACKIT Windows Servers have a Scanning Agent installed that transmits licensing-relevant data. Additionally, each Windows Server has a scheduled task that triggers the Scanning Agent.
Unfortunately, a Windows update in the past modified the scheduled task, causing the Scanning Agent to stop sending data.
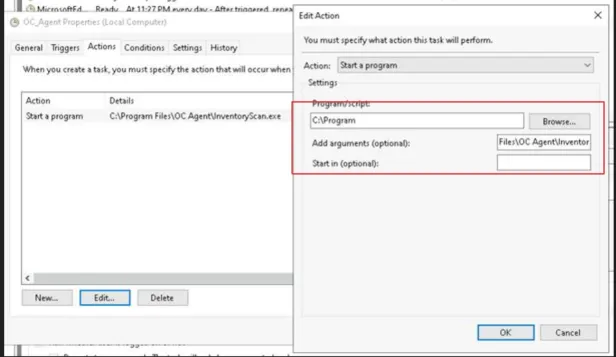
The culprit: Parts of the file path are interpreted as arguments, so the command is incomplete and the task does not start.
Solutions
Section titled “Solutions”There are two possible solutions:
- Manually via the user interface
- Using a PowerShell script
Manual solution
Section titled “Manual solution”- Open Task Scheduler and go to
OC_AgentTask. - Configure the path.
- Open Properties → Actions → Edit.
- Change the path in the input box Program/script to the following, including the quotation marks:
"C:\\Program Files\\OC Agent\\InventoryScan.exe"
- Empty the input box Add arguments (optional).
This is what it should look like when you’re done:
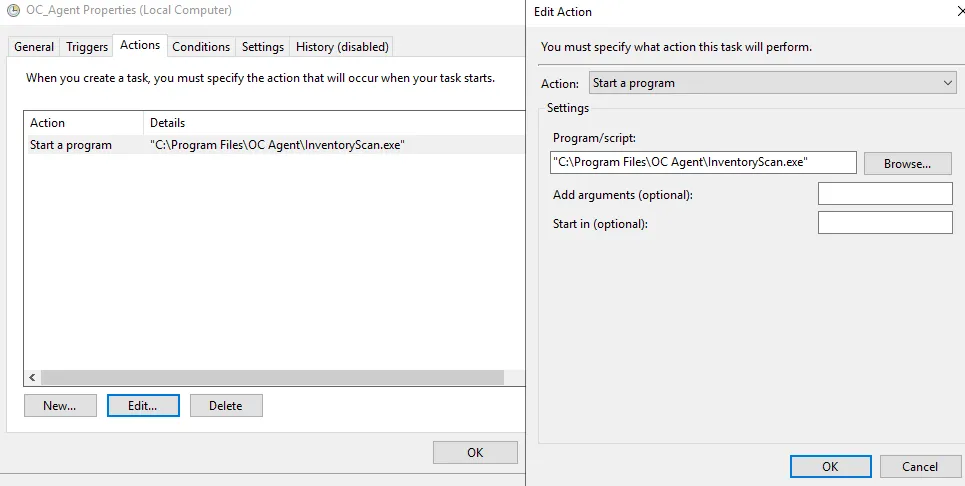 4. Click OK → OK.
4. Click OK → OK.Using a PowerShell Script
Section titled “Using a PowerShell Script”- Open PowerShell ISE with elevated permissions. Click Start then type PowerShell ISE then Right-Click on PowerShell icon and select Run as Administrator.
- Click file → New and paste the Script provided below.
- Run Script: Press F5 or the green arrow.
The Script
Section titled “The Script”Terminal window #Check if schedule task exists$task = Get-ScheduledTask -TaskName "OC_Agent"#If Task exists, set Path to correct EXE Fileif($task.TaskName -eq "OC_Agent"){$action = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "C:\Program Files\OC Agent\InventoryScan.exe"Set-ScheduledTask -TaskName "OC_Agent" -Action $action}#If Task doesn't exists, create TaskElse{& schtasks /create /SC daily /ST $((Get-Random -Maximum 24).ToString("00")+":"+$(Get-Random -Maximum 60).ToString("00")) /MO 1 /RL HIGHEST /TN OC_Agent /TR "C:\Program Files\OC Agent\InventoryScan.exe" /RU "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"}Unexpected increase of RDS license counts when using a domain
Overview
Section titled “Overview”When a customer joins a Windows Server to their domain, an unexpected increase in Remote Desktop Services (RDS) license counts may occur. The root cause is linked to the automatic or intentional nesting of users or groups into specific local groups on the Windows Server that allow local or RDP access to the machine and therefore are relevant for the monthly SPLA licensing.
Affected Local Groups
Section titled “Affected Local Groups”The unexpected increase in RDS license counts occurs if one or more users/groups are nested (e.g., via Group Policy Objects (GPO)) in any of the following local groups on the Windows Server:
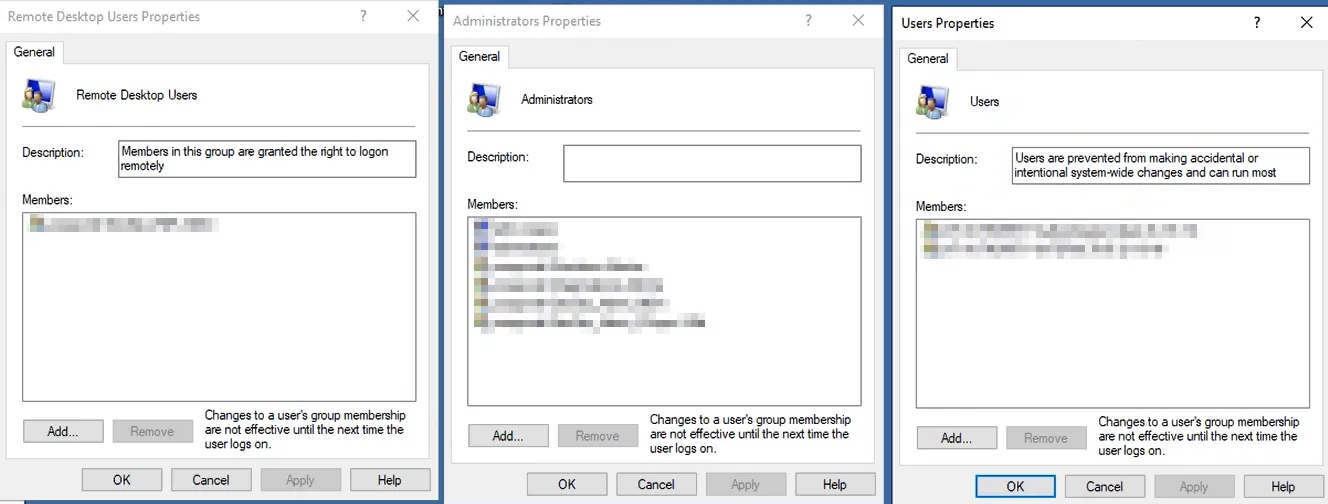
- Remote Desktop Users
- Description: Members of this group are granted the right to log on remotely.
- Administrators
- Description: Members of this group have complete and unrestricted access to the computer or domain.
- Users
- Description: Members of this group are prevented from making accidental or intentional system-wide changes and can run most applications.
Reason for the Increase
Section titled “Reason for the Increase”When a server is joined to a domain, domain users and groups may be added automatically to the above local groups via GPO or other domain management tools. This can lead to an unexpected rise in the number of users counted by RDS licensing. The SPLA reporting tool will detect these additional users or groups and report them, thus increasing the total count of RDS licenses.
Example Scenario
Section titled “Example Scenario”Consider a server that is joined to a domain. The domain GPO automatically adds certain users or groups to the local “Remote Desktop Users” group on this server. Even though these users may not actively use Remote Desktop Services, already their membership in this group will be counted by the SPLA reporting tool. Also users or groups that are i.e. added to the local “Users” group have technically access to the server by being able to log on over the console in the STACKIT Portal, thus counting as SPLA relevant and leading to an increased RDS license count.
Below is a screenshot showing the local groups on a Windows Server where users/groups may be nested:
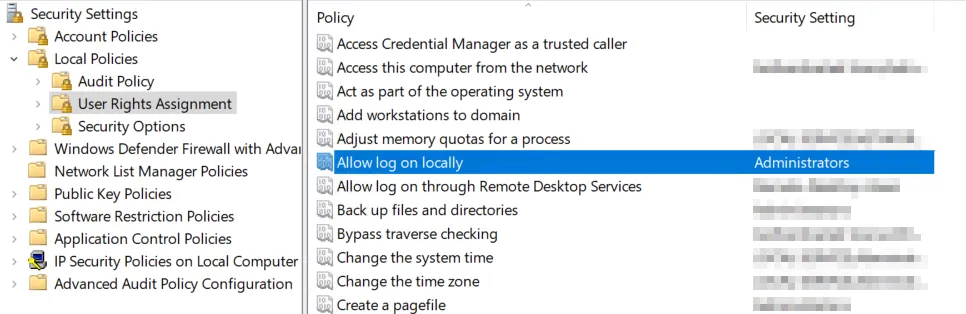
Alternative Solution:
Configure the security setting “Allow log on locally” in the User Rights Assignment of your local policy. You can define, which groups or users are allowed to log on to the system. By removing “Users”, they are technically not able to log on to the system anymore:
Recommended Actions
Section titled “Recommended Actions”- Review Group Memberships: Regularly review the memberships of the “Remote Desktop Users”, “Administrators”, and “Users” groups on servers that are part of a domain.
- Adjust GPOs: If necessary, adjust GPOs to prevent automatic nesting of large groups or unnecessary users into these local groups.
- Adjust local security setting “Allow log on locally”: You can remove specific users/groups from the local security setting “Allow log on locally” to prevent of being capable to log on locally on to the system.
- Manual Auditing: Perform manual audits on the servers to ensure that only the necessary users/groups are members of these local groups.
Windows Server does not complete first boot configuration (SNA non-routed networks)
When deploying a Windows Server VM in a non-routed SNA network, special configuration is required to ensure the instance can complete its initial setup via Cloudbase-Init. Without these settings, services such as user provisioning, OS activation, and the management tools (i.e. Octopus) may fail.
Prerequisites & Requirements
Section titled “Prerequisites & Requirements”Network Flow Overview
Section titled “Network Flow Overview”It is recommended to place a router/proxy/VPN appliance in your non-routed network with access to the routed network, and open the relevant ports mentioned further below.
VM (non-routed network)↓Firewall / VPN / Proxy (with egress rules)↓Standard network (internet/DNS/KMS)DHCP and Metadata Access
Section titled “DHCP and Metadata Access”Cloudbase-Init requires enabled DHCP to retrieve network settings and access the metadata service. Ensure that DHCP is functional and not blocked by your network device (e.g., pfSense, router, VPN gateway).
DNS Resolution
Section titled “DNS Resolution”A public DNS server must be reachable from the VM to resolve external services. Without proper DNS, the OS activation will fail and the local Cloudbase-Init script cannot complete its first-boot configuration during VM deployment.
Firewall Rules (Outbound)
Section titled “Firewall Rules (Outbound)”On your firewall, proxy, or VPN device between the VM and the routed network, make sure the following outbound ports are allowed:
Destination IP Port Purpose 193.148.162.228 TCP 4455 Microsoft Licensing Management (Octopus) TCP 1688 Windows OS Activation via KMS Security Group Configuration
Section titled “Security Group Configuration”By default, each VM is assigned a default security group that includes predefined IPv4/IPv6 rules. These rules are designed to allow outbound (egress) traffic while blocking inbound (ingress) traffic, enabling the VM to reach external services such as metadata, DNS, KMS, and the Microsoft Licensing Management during initialization.
Modifying or removing these default rules without providing equivalent custom rules may unintentionally block essential outbound traffic. As a result, the VM may fail to access critical services and can not complete the deployment.
If you choose to replace the default security group, make sure your custom rules explicitly allow outbound access to the following:
- Metadata service:
169.254.169.254 - DNS: UDP/TCP port
53 - KMS (TCP port 1688) and Octopus (TCP port 4455) to
193.148.162.228 - Optional services: e.g., NTP if required
Cloudbase-Init User Data Configuration
Section titled “Cloudbase-Init User Data Configuration”Ensure your Cloudbase-Init YAML (user data) uses correct syntax when creating the administrator account. Improper syntax can prevent the Cloudbase-Init plugin from parsing and running the configuration correctly. This will result in the VM being inaccessible (e.g., no local login possible).
Useful Links:
Summary and Checklist
Section titled “Summary and Checklist”- Proxy/Router/VPN is set up to bridge non-routed and routed networks
- DHCP is enabled and functional
- Public DNS server is reachable
- Outbound access to
193.148.162.228via:- Port 1688 (KMS)
- Port 4455 (Octopus)
- Security group rules allow outbound access to metadata, DNS, and required or optional services
- Valid Cloudbase-Init configuration with admin user included