Ensuring image integrity with immutability
Last updated on
In containerized environments, tags like latest or prod are often used as pointers to specific versions of an application. However, by default, these tags are mutable, meaning they can be overwritten by a new image push. This behavior introduces significant risk in production environments.
The problem with mutable tags
Section titled “The problem with mutable tags”The standard Docker implementation does not enforce a permanent link between a human-readable tag (e.g., my-app:v1.0) and the cryptographic digest of an image (e.g., sha256:abc...). This creates several problems:
- Loss of Trust: A tag can no longer be trusted to identify a specific, validated version of an image.
- Deployment Errors: Automated deployment systems could inadvertently deploy an unstable or incorrect version if a tag has been overwritten.
- Unintended Deletions: Deleting one tag that points to a specific digest can result in the deletion of all other tags pointing to that same digest.
To mitigate these risks, STACKIT Container Registry provides a powerful feature called Tag Immutability.
How immutability rules work
Section titled “How immutability rules work”Tag immutability allows administrators to define policies at the project level that prevent specific tags from being overwritten. When an immutability rule is in effect, any attempt to push an image with a tag that already exists and matches the rule will be rejected by the registry. This guarantees that a tag, once applied, will always point to that same image digest.
Immutability rules are configured with the following logic:
- Project-Scoped: Rules are defined within a specific project’s settings.
- OR Logic: If multiple rules are created, a tag is considered immutable if it matches any of the defined rules.
- Matching and Excluding: Rules can be configured to either match specific repository and tag patterns or to match everything except for specific patterns.
An immutable tag protects not only itself but the entire underlying artifact digest to which it is attached. This “locks” the image layers and must be considered when planning tag retention and garbage collection strategies.
Creating a tag immutability rule
Section titled “Creating a tag immutability rule”Project administrators can configure immutability rules through the STACKIT CR user interface.
- Log in to the STACKIT CR portal and navigate to the desired project.
- Select the Policy tab, and then click on Tag Immutability.
- Click the Add Rule button.
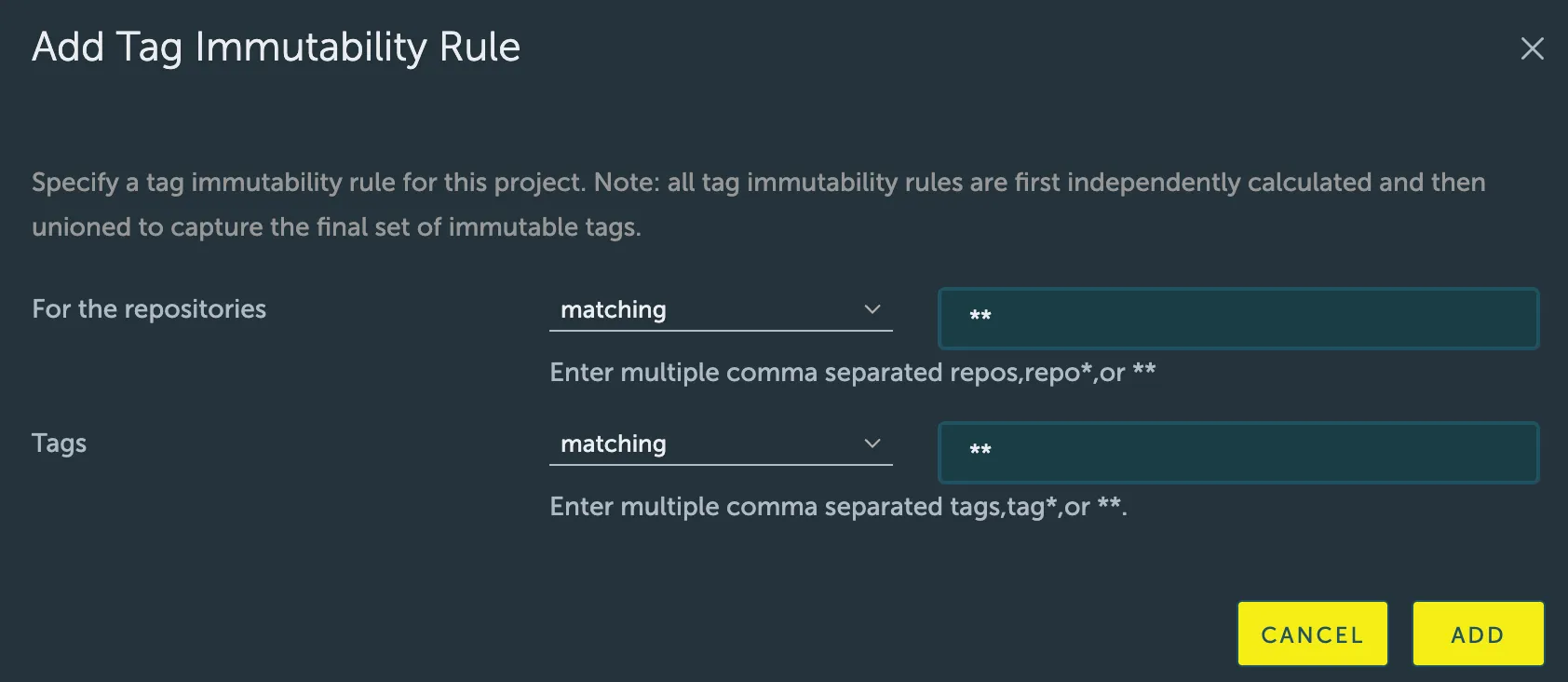
- Configure the rule using the following fields:
- Repositories: Specify which repositories the rule applies to.
- Action: Choose
matchingorexcluding. - Pattern: Enter a comma-separated list of repository names. Wildcards are supported (
**matches all repositories).
- Action: Choose
- Tags: Specify which tags the rule applies to.
- Action: Choose
matchingorexcluding. - Pattern: Enter a comma-separated list of tags. Wildcards are supported (
*matches any sequence of characters, and**matches all tags).
- Action: Choose
- Repositories: Specify which repositories the rule applies to.
- Click Add to save and activate the rule. A project can have a maximum of 15 immutability rules.
Practical examples and best practices
Section titled “Practical examples and best practices”- Make All Tags Immutable:
- Repositories:
matching,** - Tags:
matching,**
- Repositories:
- Protect Production Tags, Allow Development Overwrites: Make all tags immutable except for those named
rc,test, ornightly.- Repositories:
matching,** - Tags:
excluding,rc,test,nightly
- Repositories:
- Protect Specific Release Tags: Protect only formal release tags (e.g., following semantic versioning).
- Repositories:
matching,** - Tags:
matching,v*.*.*
- Repositories: