Create a new instance
Instantiation of a new server
Section titled “Instantiation of a new server”Within a created project, create a new server by clicking on Create server. This opens the configuration wizard.

Configuration options
Section titled “Configuration options”- Enter a name for your server under General information.
- Set the location of your new server. If you want to have redundancy by location, you can find
more information regarding the Regions and availability zones.
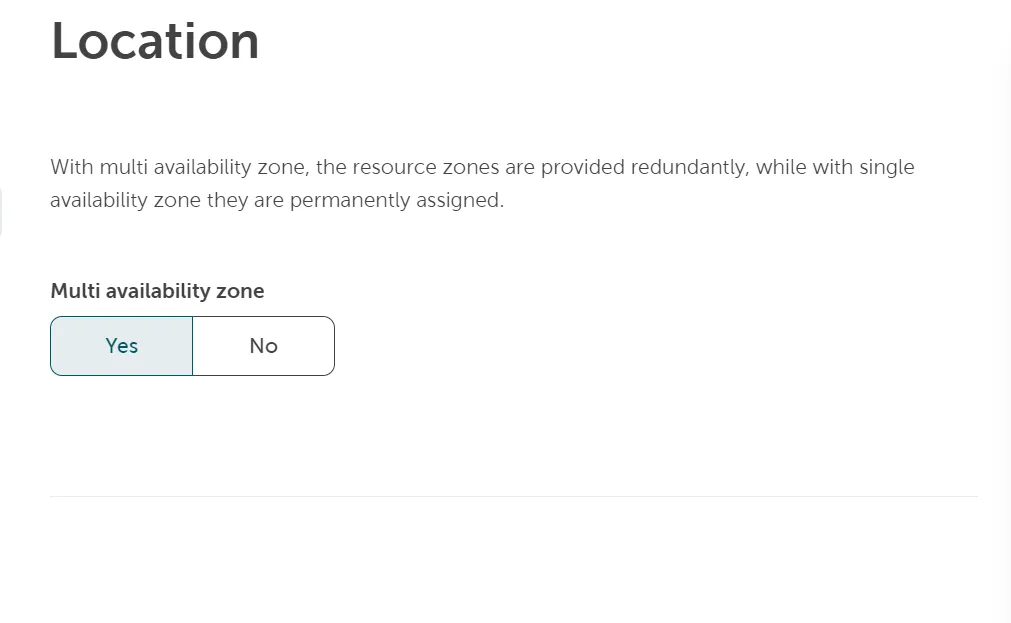
- Select the desired operating system and version from the list.
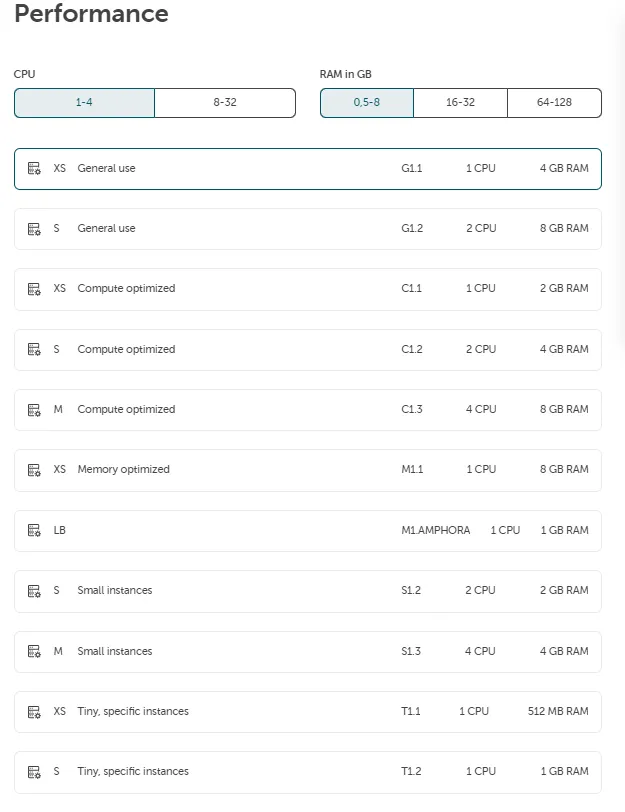
- Select the desired flavor below depending on the required performance. This includes the
number of virtual CPUs, maximum usable RAM and hard disk storage capacity. The flavors are grouped
by different use cases (General use, Processor Optimized, RAM optimized and Small packages).
Within the groupings, select the desired size (XS to XL). See:
Machine types
- Additional storage volumes can be added to the hard disk storage via Disk volumes, which can be easily attached to the server. See: Block Storage.
Configure the network
Section titled “Configure the network”The next step is to configure the network.
If a network is not already available to provide the server, a network environment can be created using Networking → Network → Enable initial network.
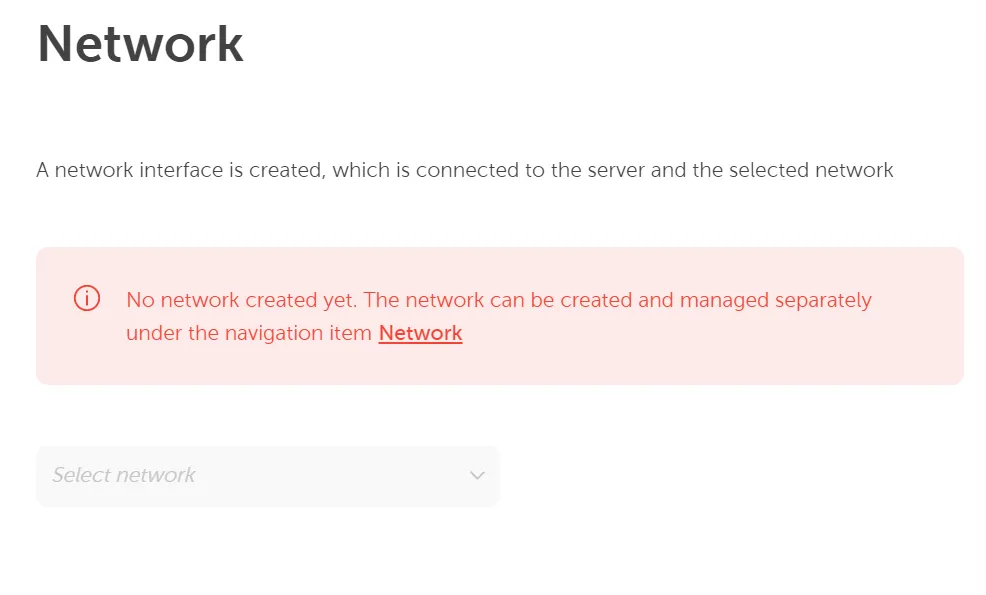

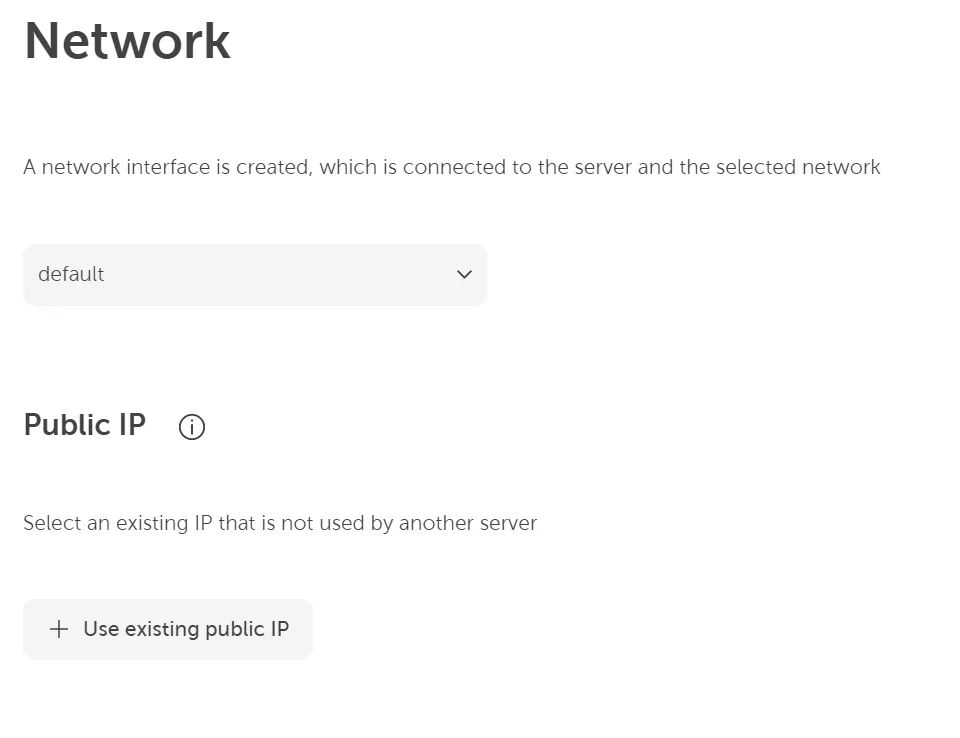
If a network is already created in this project, you can select it from the list.
A public IP address can be easily added if you already have existing ones by clicking Use existing public IP. Or you can create and assign such addresses via Networking → Network → Public IP → Create public IP on the project level. The server can be reached from outside via this address. This is described in detail here: Create public IP address.
Credentials
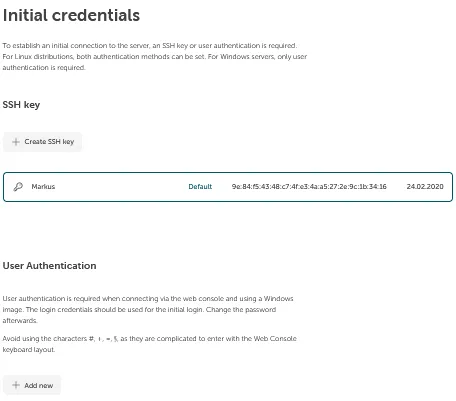
Section titled “Credentials”Finally, you can give initial credentials to the server so that you can authenticate and log in to the server afterwards (e.g., via SSH). Two options are available here:
SSH key: Clicking on Add new allows you to store a public SSH key, so you can log in to the server via SSH using the private counterpart.
User authentication: If you want to connect to the server via web console, you need initial user password credentials, as no SSH key can be used here. Create credentials by clicking on Add. You can use these credentials e.g. for the web console (see Access your server using web console).
If the server is configured as desired, it can be created by clicking on Order fee-based. After a few seconds, the new instance should appear under the Server tab with the status Running. The VM is then already started.