Troubleshooting
Last updated on
When you troubleshoot STACKIT Edge Cloud it’s important to define the scope of what it is that you’re trying to troubleshoot. We’ll define three layers, just as we did in the authentication documentation, to introduce a coherent language:
- STACKIT Platform: this are components that are entirely managed by STACKIT. Handling issues and troubleshooting on this layer is the responsibility of STACKIT.
- STACKIT Product: this are components that form the STACKIT Edge Cloud product. While STACKIT provides the resources to customers to interact with the actions performed by the customer are the customers responsibility. If there is a misconfiguration it is the customers responsibility to identify and fix the issue. Troubleshooting can be performed from both ends, depending on the issue faced.
- Managed Systems: this are the components that are entirely managed by a customer. Troubleshooting normally is the customers responsibility with the exception of STACKIT provided and managed components such as the EdgeHostLet service when using STACKIT Edge Cloud.
Please refer to the shared responsibility model to learn more about the responsibilities of STACKIT and the customer when using STACKIT Edge Cloud.
Based on at which layer the issue exists there are certain things a customer can and should do to further narrow down the root cause of the issue. This page will guide you through some of the most common issues and provide initial troubleshooting help.
STEC troubleshooting
Section titled “STEC troubleshooting”As outlined throughout this guide you manage your STACKIT Edge Cloud product by working with a set of Kubernetes Custom Resources. Namely:
EdgeImageEdgeHostEdgeClusterEdgeMachine(read only)
If there is a issue with those resources standard Kubernetes troubleshooting steps apply. This means you should check the spec and status fields of the resources involved as well as the Kubernetes events, e.g. using kubectl events, to identify issues.
Talos troubleshooting
Section titled “Talos troubleshooting”Getting you talosconfig
Section titled “Getting you talosconfig”You authenticate with Talos using a talosconfig file. Follow the next steps to get the file.
Prerequisites:
- Successfully authenticated in the UI of a STEC instance.
Steps:
-
Navigate to the Cluster section. You’ll get to the Clusters overview. Click on the name of the cluster you want to get the talosconfig file for.
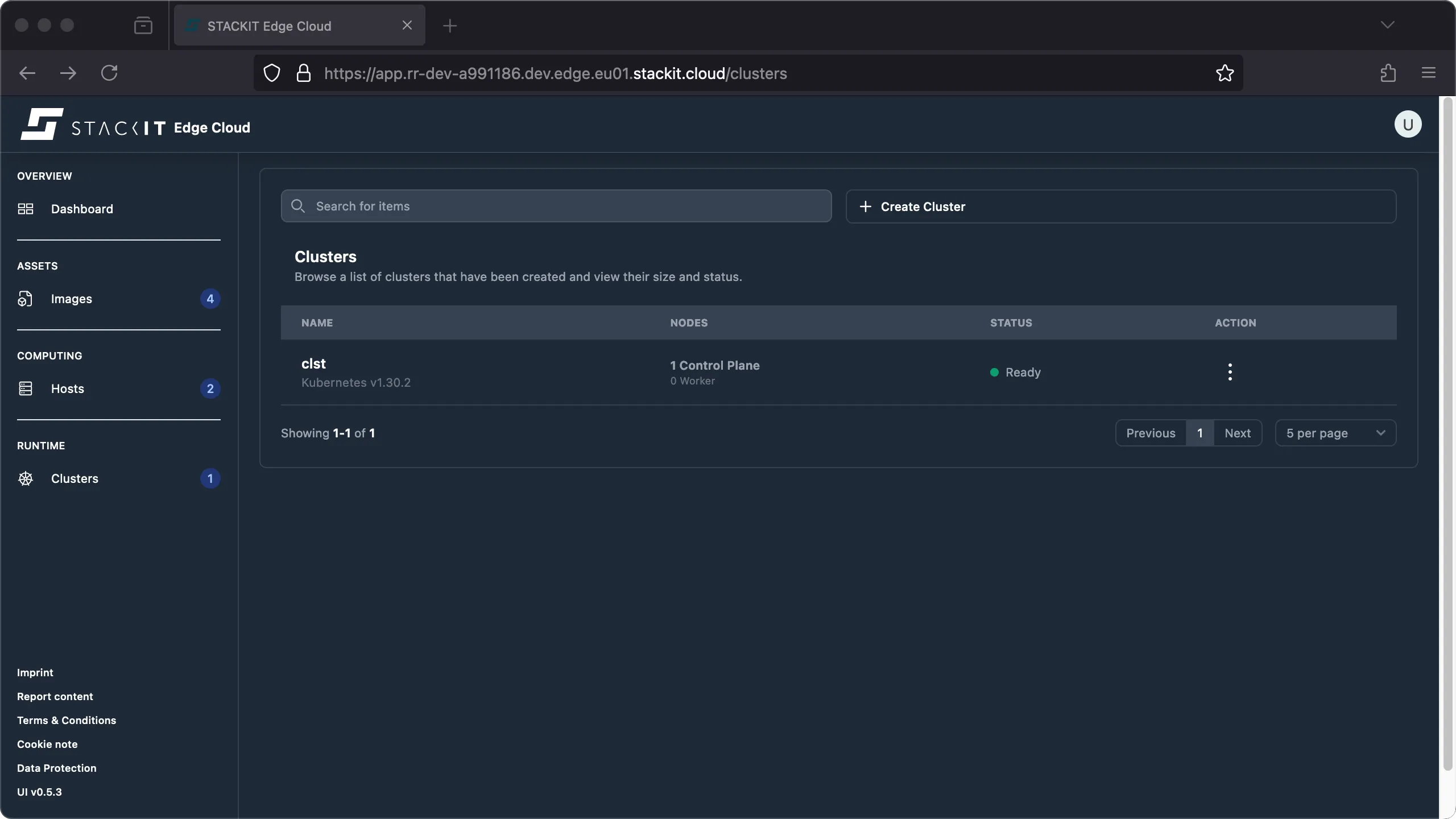
-
Click on the talosconfig button to start the download of a valid talosconfig file for the selected cluster.

Prerequisites:
- Successfully authenticated with a STEC instance.
- Tools: a generic Linux bash terminal,
kubectl,yq.
Steps:
-
The talosconfig for every cluster lives in the STEC instance as a Kubernetes secret. You simply have to get the correct secret, decode and save it to a file.
Terminal window > export KUBECONFIG=~/.kubeconfig/your-stec.kubeconfig.yaml> CLUSTER_NAME="cluster-01"> kubectl get secrets/${CLUSTER_NAME}-talosconfig --namespace default -o yaml | yq '.data.talosconfig' | base64 --decode > ${CLUSTER_NAME}.talosconfig.yaml
Using talosctl
Section titled “Using talosctl”You may use any gRPC compatible client to interact with Talos. For this example we’ll use talosctl.
Every Talos Linux node does expose an endpoint for the Talos gRPC API. When you use talosctl it will try to connect to the gRPC endpoint specified in the talosconfig. This may fail if the endpoint is not reachable. In that case you can specify a different node from the cluster you want to interact with using the --endpoints CLI parameter of talosctl, providing a IP / DNS record of that endpoint, to connect to a different endpoint.
The --nodes parameter of talosctl however always has to be specified and specifies the nodes that should be targeted by the talosctl command. If the --endpoints used are different from the --nodes used the chosen endpoint will proxy the command to all the specified nodes. A network connection from the talosctl CLI is only created to the --endpoints.
Check the talosctl documentation to learn more about how to use talosctl.
While it’s possible to use talosctl to interact with a STACKIT Edge Cloud managed cluster please be aware that you should not use talosctl to directly change the configuration of your managed systems. If you want to change the configuration of your system make sure to interact with it using the exposed STEC CRDs such as EdgeCluster, as explained in the documentation. Commands such as talosctl rollback, talosctl rotate-ca and talosctl reset can break the connection with STACKIT Edge Cloud management plane and lead to unexpected behavior. As a best practice only use commands that read information but don’t alter it.
Make sure you use the latest version of talosctl that’s supported with the Talos version of the Talos node you’re working with. In the examples below we’ve been using talosctl version 1.10.5.
Prerequisites:
- You acquired a valid talosconfig for the STEC managed Edge Cluster.
- Tools: a generic Linux bash terminal, talosctl,
yq.
Steps:
> export TALOSCONFIG=your-edge-cluster.talosconfig.yaml
> TALOS_IP=$(yq '.contexts.[ keys |.[0]].endpoints[0] | split(":") |.[0]'./my-edge-cluster.talosconfig)
> talosctl --nodes $TALOS_IP get membersNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION HOSTNAME MACHINE TYPE OS ADDRESSES192.168.4.142 cluster Member talos-4ic-txr 1 talos-4ic-txr controlplane Talos (v1.10.5) ["192.168.4.142"]
> talosctl --nodes $TALOS_IP get svcNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION RUNNING HEALTHY HEALTH UNKNOWN192.168.4.142 runtime Service apid 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service auditd 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service containerd 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service cri 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service dashboard 1 true false true192.168.4.142 runtime Service etcd 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service ext-edgehostlet 1 true false true192.168.4.142 runtime Service kubelet 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service machined 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service syslogd 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service trustd 2 true true false192.168.4.142 runtime Service udevd 2 true true falsetalosctl troubleshooting 1x1
Section titled “talosctl troubleshooting 1x1”In this section we’ll take a look on common commands that talosctl provides that you may find useful when troubleshooting.
Make sure you use the latest version of talosctl that’s supported with the Talos version of the Talos node you’re working with. In the examples below we’ve been using talosctl version 1.10.5.
Workload troubleshooting
Section titled “Workload troubleshooting”> TALOS_IP=YOUR-NODE-IP
### Get a list of all running container> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP containersNODE NAMESPACE ID IMAGE PID STATUS192.168.1.123 system apid 4614 RUNNING192.168.1.123 system ext-edgehostlet 5020 RUNNING192.168.1.123 system trustd 4760 RUNNING
### And also the (hidden) Kubernetes containers managed by Talos> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP containers --kubernetesNODE NAMESPACE ID IMAGE PID STATUS192.168.1.123 k8s.io kube-system/coredns-8477467d67-5qfxg registry.k8s.io/pause:3.10 6409 SANDBOX_READY192.168.1.123 k8s.io └─ kube-system/coredns-8477467d67-5qfxg:coredns:8465df5308fc registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns:v1.12.1 6442 CONTAINER_RUNNING192.168.1.123 k8s.io kube-system/coredns-8477467d67-lhvr2 registry.k8s.io/pause:3.10 6633 SANDBOX_READY192.168.1.123 k8s.io └─ kube-system/coredns-8477467d67-lhvr2:coredns:20456553862e registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns:v1.12.1 6677 CONTAINER_RUNNING192.168.1.123 k8s.io kube-system/kube-apiserver-foobar registry.k8s.io/pause:3.10 5219 SANDBOX_READY...
### You may also want to get a list of all container images> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP images listNODE IMAGE DIGEST SIZE CREATED192.168.1.123 ghcr.io/siderolabs/flannel:v0.26.7 sha256:288b45ff822c72526a35f518ac9a1f84d43d52c52ed7685fa4bf8d54cf537848 32 MB 2025-09-05T14:07:26Z192.168.1.123 ghcr.io/siderolabs/flannel@sha256:288b45ff822c72526a35f518ac9a1f84d43d52c52ed7685fa4bf8d54cf537848 sha256:288b45ff822c72526a35f518ac9a1f84d43d52c52ed7685fa4bf8d54cf537848 32 MB 2025-09-05T14:07:26Z...Configuration troubleshooting
Section titled “Configuration troubleshooting”> TALOS_IP=YOUR-NODE-IP
### Verify currently applied machineconfig> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP get machineconfig -o yaml > machineconfig.yaml
### Use yq to get a more readable version of the configuration> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP get machineconfig -o yaml | yq.spec > machineconfig.yaml
### The machine config makes use of at least one specified installation disk and network interface.### You may use the following commands to get a better understanding of the hardware and to verify the machineconfig is using the correct devices.
### Get a list of the local disks> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP disks > talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP disksNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION SIZE READ ONLY TRANSPORT ROTATIONAL WWID MODEL SERIAL192.168.1.123 runtime Disk loop0 2 4.1 kB true...192.168.1.123 runtime Disk vda 2 34 GB false virtio true
### Get a list of the network interfacestalosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP get ethernetstatusNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION LINK SPEED192.168.1.123 network EthernetStatus bond0 1 false192.168.1.123 network EthernetStatus enp0s1 2 true...
### And the addresses assigned to those...talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP get addressesNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION ADDRESS LINK192.168.1.123 network AddressStatus enp0s1/192.168.1.123/24 1 192.168.1.123/24 enp0s1...System troubleshooting
Section titled “System troubleshooting”> TALOS_IP=YOUR-NODE-IP
### Get the Talos version to make sure you're using the correct version of the Talos documentation before you start> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP get versionNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION VERSION192.168.1.123 runtime Version version 1 v1.10.5
### Access the Talos dashboard to get a quick first overview of the system status> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP dashboard
### Check the time configuration for possible time drift issuestalosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP timeNODE NTP-SERVER NODE-TIME NTP-SERVER-TIME192.168.1.123 time.cloudflare.com 2025-09-08 12:12:21.957193374 +0000 UTC 2025-09-08 12:12:21.944392958 +0000 UTC
### Check individual Talos services> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP servicesNODE SERVICE STATE HEALTH LAST CHANGE LAST EVENT192.168.1.123 apid Running OK 1h25m9s ago Health check successful192.168.1.123 auditd Running OK 1h25m11s ago Health check successful192.168.1.123 containerd Running OK 1h25m11s ago Health check successful...
### For example you may want to check the state of etcd> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP logs etcd -f192.168.1.123: {"level":"info","ts":"2025-09-08T12:30:30.905141Z","caller":"mvcc/index.go:214","msg":"compact tree index","revision":21473}...
### Since a service doesn't neccessary fail but may also misbehave, you may want to check the service logs.### This is possible for all services that are running. Otherwise use the health command.### Get the logs of a running service> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP logs <service> -f
### Get the service status and an overall health overview> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP healthdiscovered nodes: ["192.168.1.123"]waiting for etcd to be healthy:...waiting for etcd to be healthy: OKwaiting for etcd members to be consistent across nodes:...waiting for etcd members to be consistent across nodes: OK...
### If errors occure on the system level and not within a service you might find error logs in the Talos Linux Kernel logs.### Get the log messages that would normally show up on the dashboard> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP dmesg | less192.168.1.123: user: warning: [2025-09-08T12:30:06.931234263Z]: [talos] apply config request: mode auto(no_reboot)192.168.1.123: kern: notice: [2025-09-08T12:30:06.932811263Z]: XFS (vda3): Mounting V5 Filesystem 529e1e52-7e80-48bb-8cec-9821fef058ae192.168.1.123: kern: info: [2025-09-08T12:30:06.940238263Z]: XFS (vda3): Ending clean mount...
### Talos Linux makes use of the Common Operating System Interface (COSI) specification to expose system resources.### For troubleshooting it might be useful to get a list of the available system resources you can use to get a full overview of the effective system configuration.### Get the list of all Talos resources that you can get using the 'get' command> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP get rdNODE NAMESPACE TYPE ID VERSION ALIASES192.168.1.123 meta ResourceDefinition acquireconfigspecs.v1alpha1.talos.dev 1 acquireconfigspec acs192.168.1.123 meta ResourceDefinition acquireconfigstatuses.v1alpha1.talos.dev 1 acquireconfigstatus acs192.168.1.123 meta ResourceDefinition addressspecs.net.talos.dev 1 addressspec as192.168.1.123 meta ResourceDefinition addressstatuses.net.talos.dev 1 address addresses addressstatus as...
### There are also commands for reboot (and reset), if needed.### Be aware that the reset of a system will fully reset it to it's initial configuration and this might not be what you want to do.> talosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP reboot
### Create a support bundle for further analysistalosctl -e $TALOS_IP -n $TALOS_IP support --output talos-support.zip1s [==================] 100% 192.168.1.123: collect udevd.stateSupport bundle is written to talos-support.zip