Create databases
Last updated on
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”In order to follow the steps described on this page, the following conditions need to be met:
-
Your organization has a customer account.
(See: Create a customer account) -
You have a User Account with the necessary permissions.
(See: Create a user account) -
You have a Project in your customer account.
(See: Create a Project) -
You have created a Service Account.
(See: Create a Service account) -
You have assigned the required project permissions to this service account.
(See: Assign permissions to a service account) -
You have created an Access Token for this service account.
(See: Assign authentication token to a service account) -
You have created a SQLServer Flex Instance.
(See: Create a SQLServer Flex Instance) -
You are connected to the SQLServer Flex Instance.
(See: Connect to a SQLServer Flex Instances) -
You previously created a user and assigned the right server role to it.
(See: Create user)
(See: Server and project roles and permissions)
Considerations for Creating Databases on SQLServer Flex
Section titled “Considerations for Creating Databases on SQLServer Flex”-
Database naming:
Database names can only contain alphanumeric characters (a-z,A-Z,0-9without umlauts)
together with “_”, other special characters or space are not allowed.
Database names should not be longer than 80 characters. -
Database options / parameters:
The creation of databases is currently supported by specifying the database name, the owner, the compatibility level and the collation as parameters. -
Database initial:
When creating databases via Portal or API, the databases are being created with two files only (1 data file and 1 log file).
When creating databases using Transact SQL (T-SQL), you can set up the databases yourself.
However, the files should only be created in certain locations, whereby the following recommendations apply for better hard disk management:- Data files must be created in the following location:
/var/opt/mssql/custdata/. - Log files must be created in the following location:
/var/opt/mssql/custlog/. - It is best not to enter any path information when creating (on PRIMARY / LOG on).
Databases can not be created with files less than:
- 128 MB for data files with auto-growth of 64 MB.
- 64 MB for log files with auto-growth of 64 MB.
- Data files must be created in the following location:
-
Database collation:
Databases can be created with any customized collation value.
However please keep into consideration that the server collation value is fixed at the current release with value:SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS,
so the tempdb collation will always beSQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. -
Database compatibility level:
The Database Compatibility Level sets the Database in the proper feature level mode for the SQLServer.
This means, that the SQL Server will run this Database with the features developed for the defined compatibility level. -
Database recovery model:
Databases should always be inFULLrecovery model in order to guarantee the RPO level defined in SLA.
Create a Database
Section titled “Create a Database”- Navigate to SQLServer Flex and select the database server on which you want to create a database.
- Create the database user for your new database.
See: Create Logins and Users in SQLServer Flex Instances - Select Databases from the menu.
- Click Create Database.
- Enter the database details in the form.
See: Considerations for Creating Databases on SQLServer Flex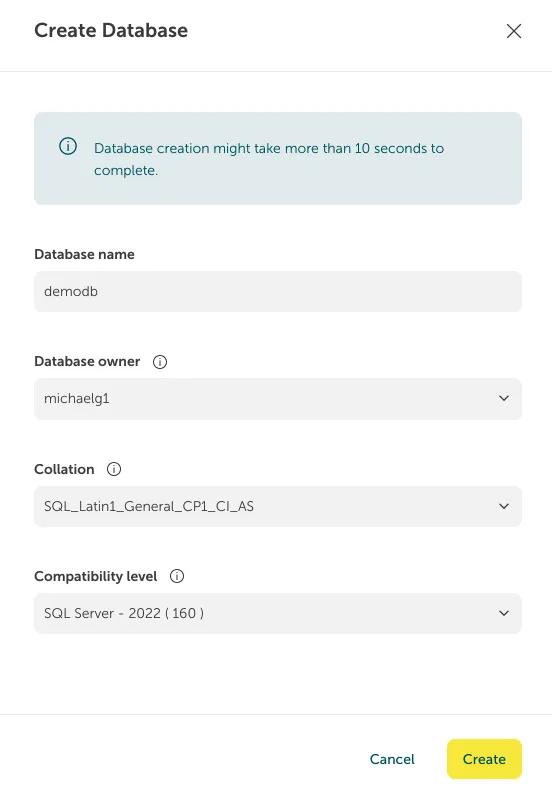
- Click Create.
For example, you can download Postman here
- Prepare the JSON payload, which is a simple JSON object containing the name of the database and the name of the database owner:
{"name": "dbname","collation": "Latin1_General_CI_AS","options": {"owner": "DBUser","collation": "Latin1_General_CI_AS","compatibility_level": "160"}}
- Open Postman and create a new Workspace.
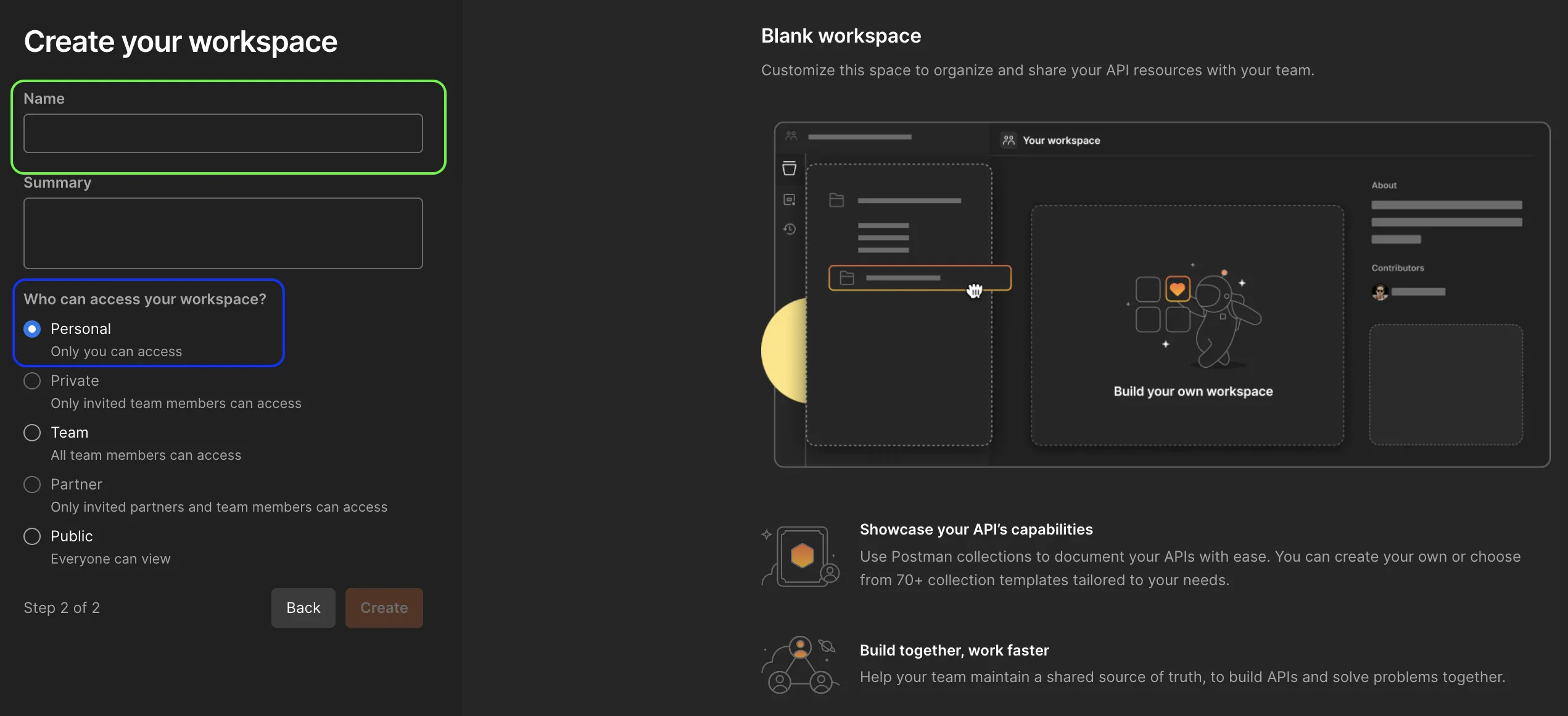
- Name the new Workspace and define the access.
- Go to Collection and press the ”+” sign to create a new API request.
- In the request window, select the POST option from the drop-down-list.
The needed compatibility Level can be fetched form the API Endpoint:
https://mssql-flex-service.api.eu01.stackit.cloud/v1/projects/{projectId}/versions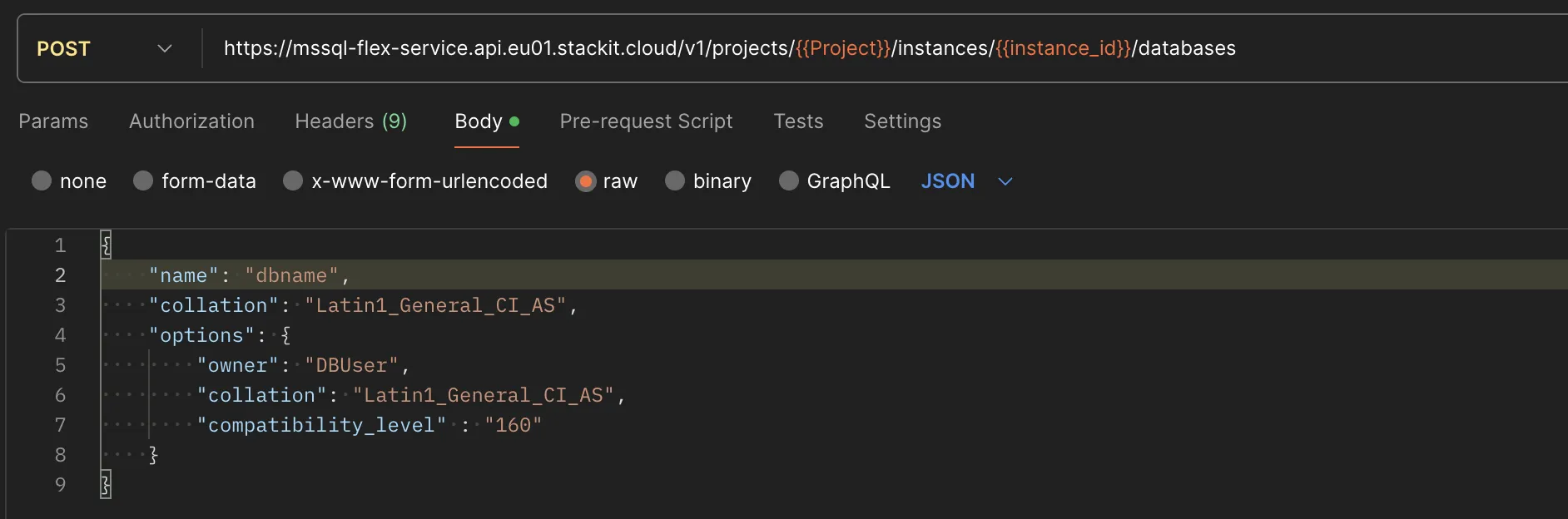
- Paste the endpoint URL into the address bar:
https://mssql-flex-service.api.eu01.stackit.cloud/v2/projects/{PROJECT_ID}/regions/{REGION}/instances/{INSTANCE_ID}/databasesand replace{PROJECT_ID},{INSTANCE_ID}and{REGION}with the project ID and the instance ID of your SQL Server instance, respectively. - Where do I find the Project ID?
The project ID is displayed in the projects list of the Resource manager: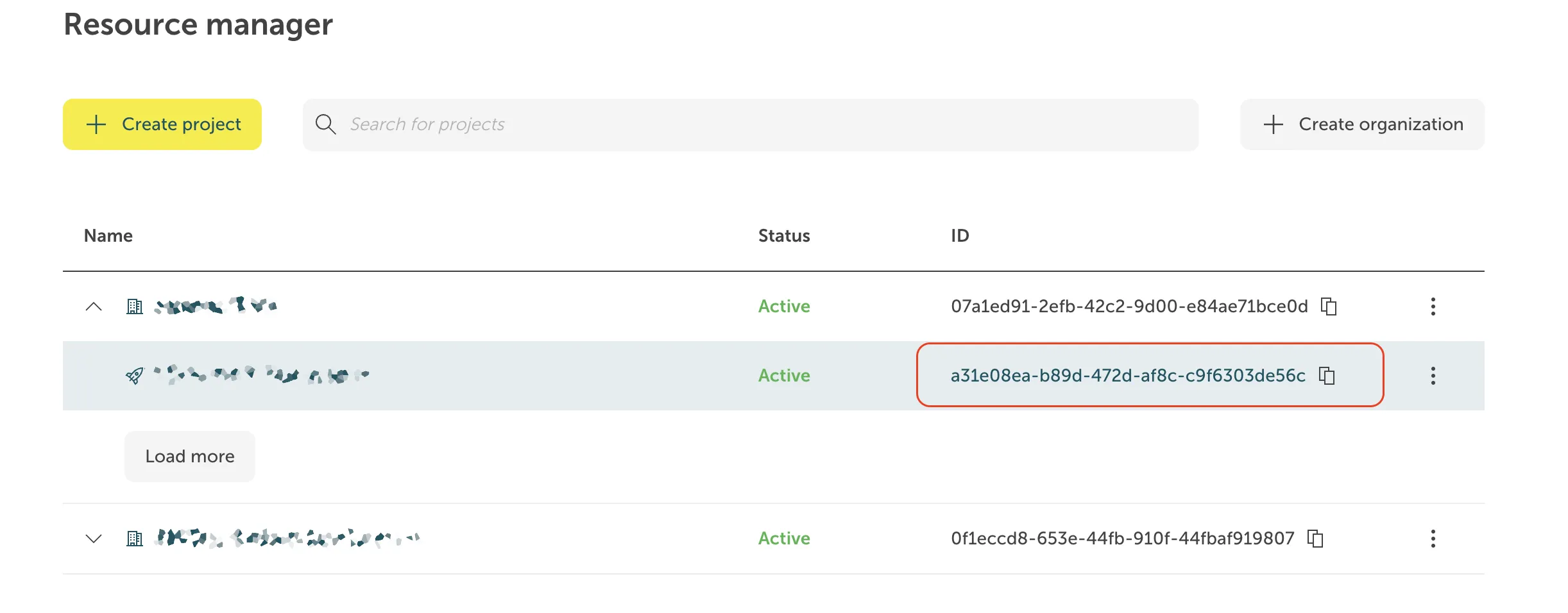 Where do I find the Instance ID?
Where do I find the Instance ID?
The instance ID has the form of a UUID. It is displayed in the Overview tab of your instance in the STACKIT Portal, in the section General information.
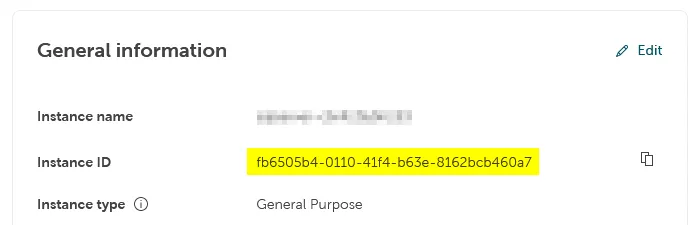 For some products, the display of the instance ID in the Portal is not implemented yet.
For some products, the display of the instance ID in the Portal is not implemented yet.
In these cases the instance ID is visible as part of the instance URL in the address field of your browser when you are on the instance page in the Portal, and it can be copied from there:
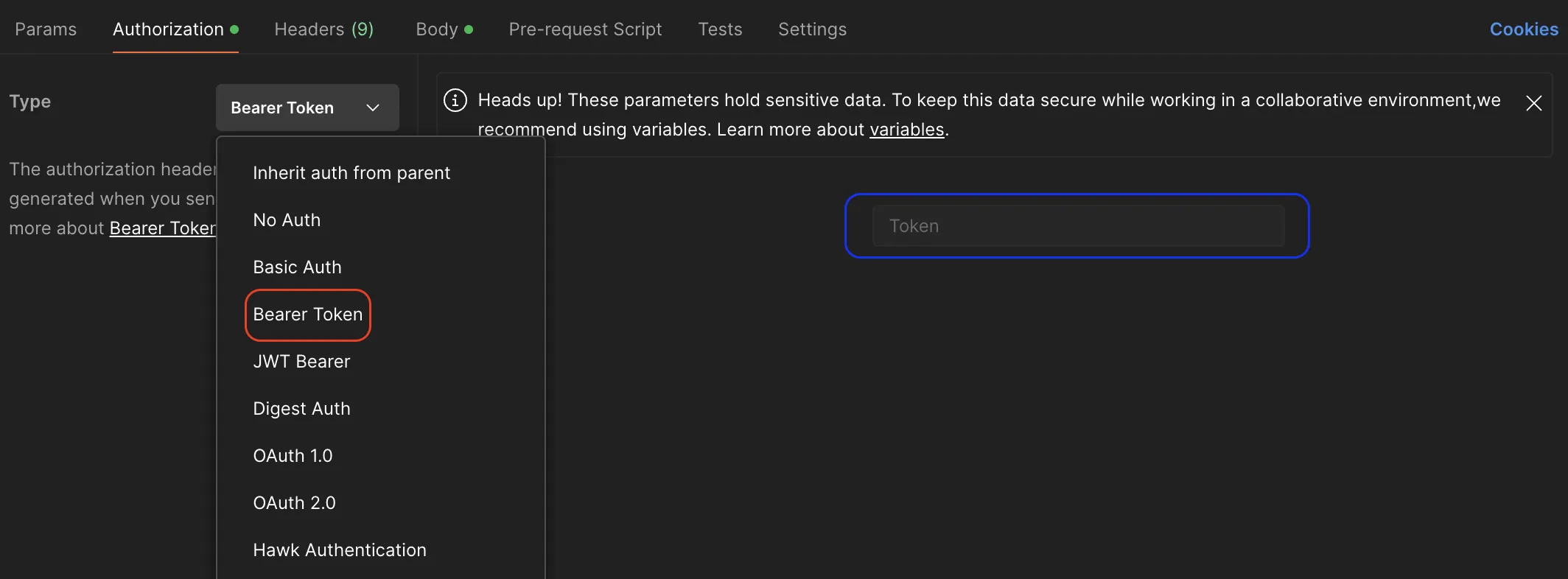
- Go to Authorization section and select Bearer Token from the Type drop-down list.
- Copy your token and past it into the Token section to be used in authentication process when executing the API.
- Select the _Body* tab.
- Select raw and paste the JSON payload you prepared before into the input area.
- Send the request.
- Open a terminal and paste the code below.
- Replace
{PROJECT_ID},{INSTANCE_ID},{REGION}and{TOKEN}with the project ID, the instance ID and the token of your SQL Server instance the database should be created in. - Replace
demo_db_1with the database name andAdministratorwith the database owner name of your choice having##STACKIT_DatabaseManager##permissions. - Run the code.
-
For macOS / Linux
Terminal window curl --location --request POST 'https://mssql-flex-service.api.eu01.stackit.cloud/v2/projects/{PROJECT_ID}/regions/{REGION}/instances/{INSTANCE_ID}/databases' --header 'Accept: application/json' --header 'Authorization: Bearer {Token}' --data '{"name": "demo_db_1","options": {"owner": "Administrator","collation": "Latin1_General_CI_AS","compatibility_level": "160"}}' | jq. -
For Windows
Terminal window curl --location --request POST 'https://mssql-flex-service.api.eu01.stackit.cloud/v2projects/{PROJECT_ID}/regions/{REGION}/instances/{INSTANCE_ID}/databases' --header 'Accept: application/json' --header 'Authorization: Bearer {TOKEN}' --data '{"name": "demo_db_1","options": {"owner": "DBAdmin","collation": "Latin1_General_CI_AS","compatibility_level": "160"}}' | ConvertFrom-Json | ConvertTo-Json
-
Some functions within Contained Availability Groups (HA) via SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) are not natively supported in Microsoft SQLServer versions < 2025,
we offer stored procedures as an efficient alternative without having to take the detour via the cloud Portal.
The stored procedures can be used on the STACKIT Flex SQLServer instances (Single and HA),
whereby on Single Instances the option is also supported via the native SQLServer client tools, e.g. SQL Server Management Studio, Azure Data Studio or any other client tool that supports connection to SQL Server.
| SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) | Azure Data Studio |
|---|---|
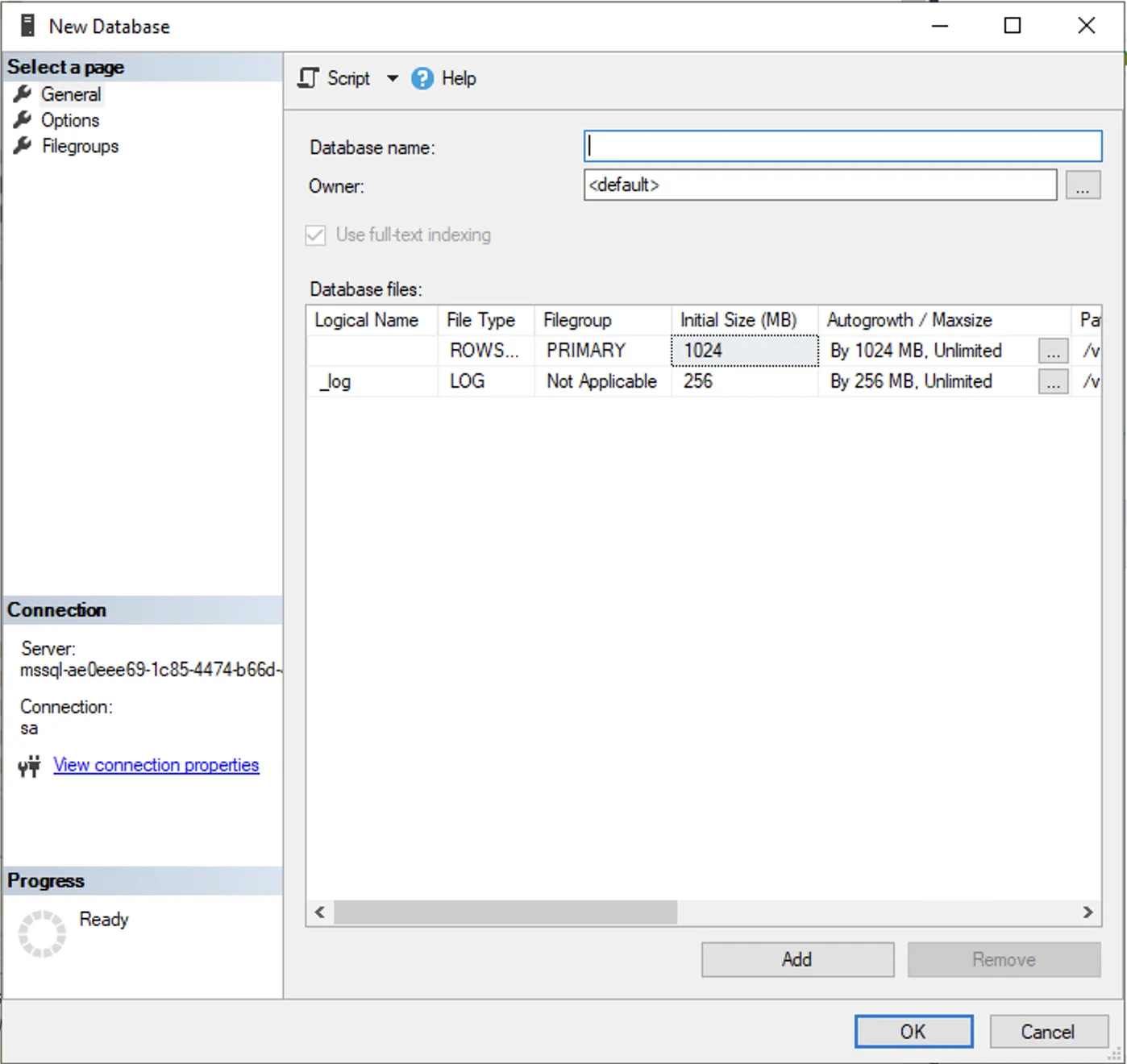 | 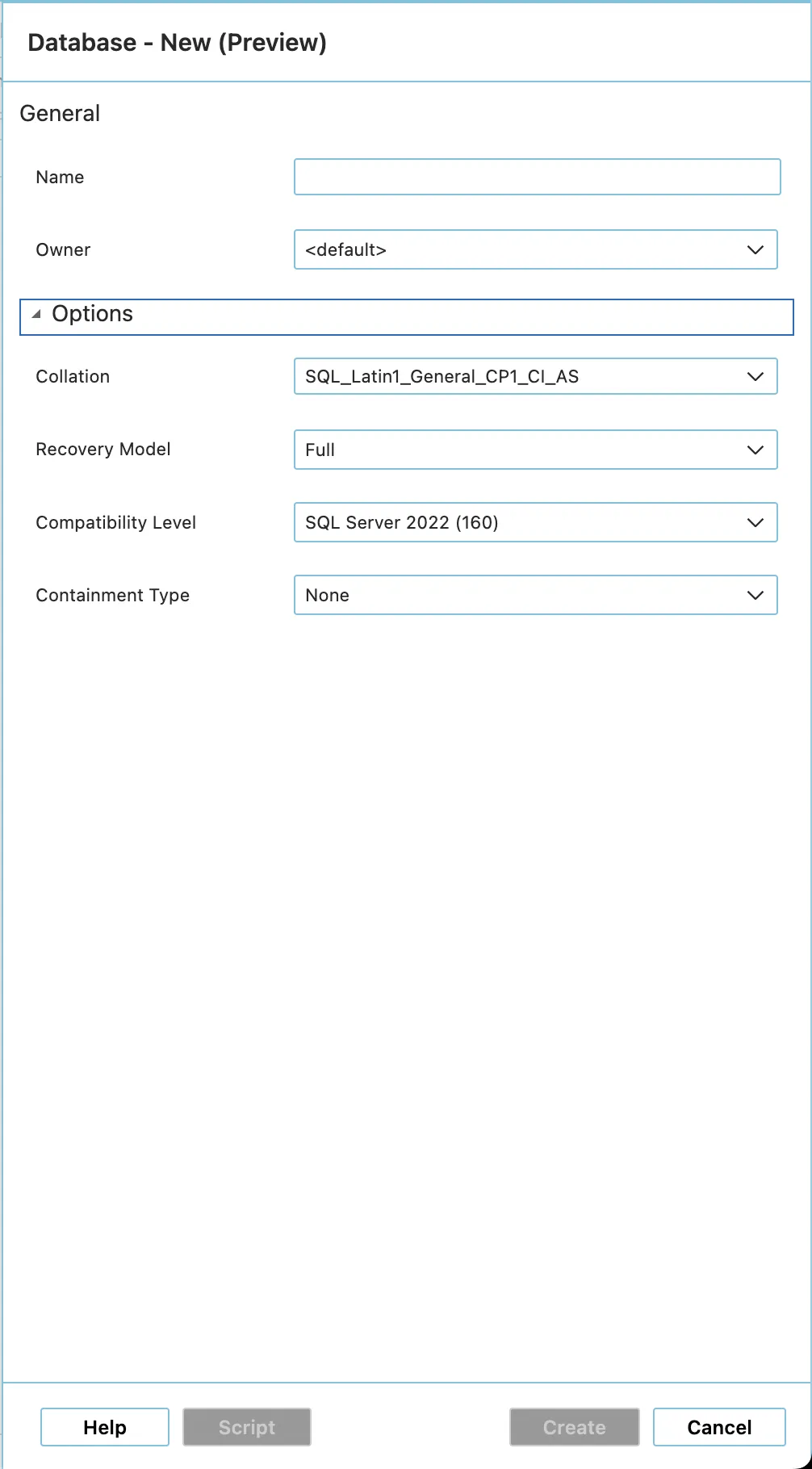 |
You can use any SQL Server query run tool that can run T-SQL against an SQL Server, e. g. SQL Server Management Studio, Azure Data Studio, or PowerShell.
-
Single Instance
- Run the
CREATE DATABASET-SQL command. For more insights about CREATE DATABASE command and options, please visit Microsoft official documentation for SQL Server. - You can also use the stored procedure provided by us, see 2. .
- Run the
-
Replica Instance (HA - Contained Availability Group)
- Databases can be created with the stored procedure
[msdb].[stackit].[create_database]. - Parameter description
The procedure accepts various parameters to adapt the database to your requirements
Parameter SQL data type Mandatory Default value Description @database_nameNVARCHAR(80)Yes - Name of the database (observes naming conventions). @owner_nameNVARCHAR(128)No Current user The database owner. @database_size_mbINTNo 128 Initial size of the data files in MB (min. 128MB). @log_size_mbINTNo 64 Initial size of the log file in MB (min. 128MB). @number_of_filesINTNo 1 Number of data files (min. 1). @collation_nameNVARCHAR(128)No SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_ASSort order of the database. @compatibility_levelINTNo Max. of instance Compatibility level of the SQL engine. - Examples
- Minimum configuration (default)
If you only specify the name, all optimizations (such as a minimum size of 128MB) are applied automatically.EXEC [msdb].[stackit].[create_database]@database_name = 'demo_db_1'; - Extended configuration
The parameters can be individually controlled for specific requirements.EXEC [msdb].[stackit].[create_database]@database_name = 'demo_db_1',@owner_name = 'Administrator',@database_size_mb = 128,@log_size_mb = 64,@number_of_files = 8,@collation_name = 'SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS',@compatibility_level = 160;
- Minimum configuration (default)
- Databases can be created with the stored procedure